Remote Monitoring And Maintenance: Why You Should Implement It Today
What Is Remote Monitoring and Maintenance?
Remote monitoring and maintenance (RMM) is an IT tool that allows managed service providers (MSPs) or a dedicated in-house department to monitor corporate devices, networks, and endpoints. If your business runs a remote team, these tools allow the IT department to collate relevant information and analytics necessary to protect employee and customer data.
RMM is not a new concept and has been gaining traction in the business world for some time. The emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic has spurred an increased interest in remote work solutions as society struggles to minimize the spread of the virus.
The benefits of a remote workforce make it a certainty that RMM systems will continue to be implemented long after COVID-19 is defeated.
Remote monitoring and maintenance are made possible by information technology (IT) tools that reside on a customer’s computer systems and servers. These RMM systems monitor all activity on each system and provide the necessary information and analytics required to address any issues that might come up.
You might see RMM referred to by other terms. The practice is also called remote IT maintenance, network management, and proactive monitoring. These terms are all used to describe solutions and methodologies designed to minimize downtime by enabling technical teams to resolve problems remotely.
How Does Rmm Work?
Remote monitoring & maintenance system usually uses several software components to identify, report, and fix technical issues affecting a company’s network. The RMM software can be installed on any application or device the business uses.
A typical RMM operates in the following algorithm:
- • It collects relevant information about the client’s computing systems and software.
- • It keeps track of the network’s conditions and monitors client endpoints.
- • After tracking, it provides activity reports about the state and health of the company’s systems.
- • With automated maintenance checks, the RMM system provides remote support and rectifies issues affecting the company’s software.
Businesses often use the remote maintenance solution to update their operating system, keep hard disks clean, and add useful antivirus definitions. This software also allows the technical team to collate and organize user data, generate reports, and automate system functions based on custom requests.
Typical Rmm System Structure
A typical RMM system is made up of several components. They work together to furnish the information necessary when implementing remote monitoring and maintenance.
There are three main parts that you will find in a viable remote maintenance software solution.
Web interface – The web interface provides a method of accessing the Internet and private networks without the need for a web browser. Using a built-in web interface simplifies the process of accessing connected systems and saves time for the remote technical team. It also promotes standardization across the team as all members access systems in the same way.
Administrator’s console – The administrator’s console is the heart of an RMM system. The console is installed on specific workstations or servers in the computing environment. It is used to perform multiple functions related to remote monitoring, maintenance, and management.
These include:
- • Defining policies and baselines that are used for monitoring an organization’s systems and applications.
- • Configuring endpoints and responding to any issues identified through monitoring.
- • Responding to tickets submitted by users or generated automatically by monitored endpoints.
RMM agent – RMM agents collect data from infrastructure endpoints. All endpoints including workstations, servers, and mobile devices need to have an agent installed to enable monitoring.
The agent regularly communicates with the administrator console regarding the status and health of the monitored entity. Alerts are generated immediately when issues are identified and action is required by the remote support team.
Outsourcing Rmm to Msps vs In-House Remote Maintenance
While remote monitoring and maintenance allow for a high degree of automation, it often involves a great deal of technical know-how and additional complexities the company may need help to handle.
As a result, organizations often have to decide between two choices: being completely responsible for in-house maintenance or outsourcing these responsibilities to managed service providers (MSPs).
Many large corporations prefer to outsource their maintenance services, allowing the company to channel its resources and time into other assets. MSPs often offer cost-effective and expert solutions with 24/7 technical support. They also possess a lot of industry knowledge and networks that enable them to provide excellent services when needed.
Companies may also decide to maintain in-house teams as it allows the staff to grow familiar with the company’s internal structure and become dedicated to keeping the company’s network pick performance.
To determine whether your company should outsource or maintains in-house teams, you can consider factors like cost, staffing flexibility, expertise, work quality and load, core business focus, response time, staff turnover, and redundancy in management roles.
What Are the Benefits of Rmm Tools?
Remote monitoring and maintenance tools address multiple issues that plague modern businesses. Implementing a robust RMM system can have a substantial impact on business operations and profitability. Following are some of the more important benefits of remote maintenance software.
Minimizing Downtime
Downtime affecting an organization’s computer systems and its associated costs to a business makes remote maintenance a very attractive solution. According to Gartner, companies can lose hundreds of thousands of dollars per hour of downtime, making it a top priority to address issues quickly to avoid outages.
According to Information Technology Intelligence Consulting (ITIC), over 25% of respondents lost between 300 and 400 thousand dollars per hour of downtime. Unless you are in the business of printing money, this is an unacceptable state of affairs.
The accompanying chart shows how expensive an hour of downtime can be for a company.
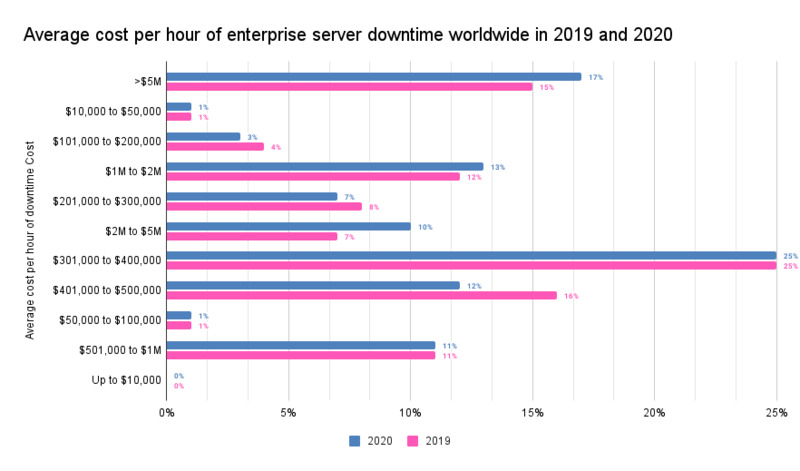
RMM systems address this problem and allow companies to act promptly when an outage occurs. The speed with which issues can be resolved can save a business a substantial sum of money by bringing systems back online quickly and minimizing the impact on its customers.
Predictive Maintenance
Remote monitoring and maintenance can be instrumental in identifying potential problems before they can impact the business. Reports generated from the data captured by RMM agents can uncover patterns that predict maintenance is required on the monitored device.
Addressing these issues proactively saves time and money by averting outages and performance issues before they become major problems. A system of predictive maintenance can extract the maximum value from a computing environment while minimizing unexpected downtime.
Improved Security

Security is a critical consideration across all areas of a company’s IT infrastructure. Data breaches can be very expensive and compromise sensitive customer information. Industries subject to regulatory standards like HIPAA or PCI can face substantial fines for implementing ineffective security measures.
Data breach costs rose from USD 3.86 million to USD 4.24 million, the highest average total cost in the 17-year history of the IBM report.
RMM technology can help an organization improve its IT security standing. Enabling trained technicians to access endpoints remotely eliminates the need to have onsite personnel with less expertise address problems. This bolsters security by limiting system access to a controlled group of employees.
Compromised credentials are responsible for the majority of data breaches. Through the use of RMM security solutions, tighter control can be asserted over who can access sensitive systems and the information they contain. The ability to quickly resolve system and network problems also contributes to better IT security by maintaining an intact infrastructure.
Enhanced Efficiency
Efficiency and productivity are critically important factors for most businesses. Remote monitoring and maintenance systems address both of these concerns and offer a viable method of improving both productivity and efficiency across an organization.
The RMM system eliminates the need for onsite visits to resolve issues with monitored endpoints. Travel time and money are saved while systems are fixed more promptly than with traditional physical visits to affected systems. Team productivity benefits from the reduced time necessary to handle problems leading to greater customer satisfaction.
Optimizing the Total Cost of Ownership
An infrastructure element’s total cost of ownership (TCO) takes into account many factors besides the required capital investment. The chart below illustrates the most common issues that affect the reliability and accessibility of an organization’s computer systems.
Based on the report published by Information Technology Intelligence Consulting, you can see that security flaws and human error are the two most prevalent causes of downtime.
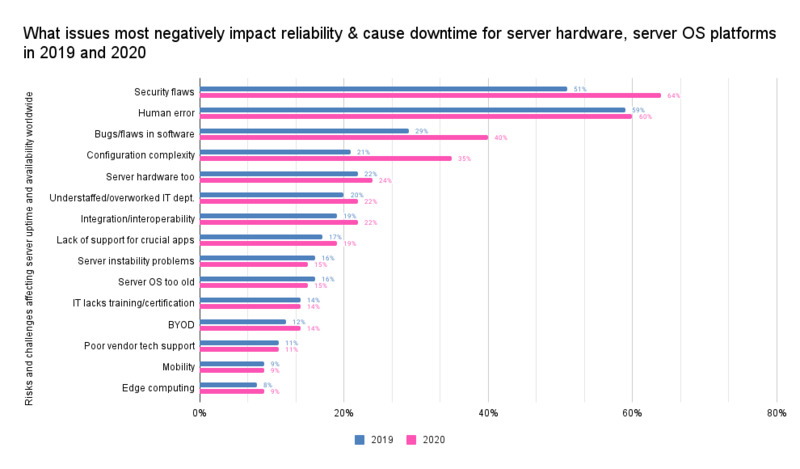
RMM systems can help increase security and minimize human error by enabling technical teams to handle problems from a centralized location. For these reasons, remote monitoring and maintenance can help reduce TCO by keeping systems running smoothly and securely.
What Rmm Software Features to Pay Attention To?
Here are the four most beneficial features to look out for when selecting an RMM that will save your business time and resources.
1. Patch management
Software patches are helpful because they allow the support team to correct bugs, address vulnerabilities, and prevent errors due to memory usage and data storage. To maintain the company’s security, all patches must be updated with the latest protocols.
Remote monitoring systems can document and report on the quality of all patches. In instances where there is an intrusive issue, the system reports the information directly to your support team.
2. Remote Access
With the rise of remote working teams, it becomes increasingly important for organizations to maintain their networks remotely. By using an RMM system, technical teams can easily access a user’s device when they need to fix an issue, making it easier to reduce labor and pinpoint potential errors.
3. Alerting System
In-house support specialists or MSPs need to keep tabs on updates and errors to maintain a reliable network server. RMMs evaluate the health of the company’s network and send alerts when necessary. This automatic monitoring allows the support team to increase customer satisfaction by providing proactive security services and network maintenance.
4. Reporting Dashboard
One key feature necessary for long-term business health and growth is reports. RMM reports allow the technical team to verify the system’s health status and compile relevant data that helps the business make informed decisions.
Summing Up
The benefits of RMM solutions help address the needs of modern businesses as they grapple with the unique aspects of a remote workforce.
Maintaining the company’s assets in check and knowing how to deal with system failures or asset breakdowns is vital not just for SMBs (small-to-medium-sized businesses) but for large enterprises as well.
RMM decreases downtimes and enhances productivity. It helps with most break-fix issues an organization may experience, brings customer service to a new level, and boosts the company’s scaling-up potential.