Top Bring Your Own Device Security Risks and Mitigating Strategies
BYOD keeps bringing about significant opportunities and challenges for businesses. So, it’s crucial for businesses to assess BYOD risks and create a BYOD risk-management strategy that really works.
This article will highlight all the possible risks and challenges your company may face, and endeavor to guide you through how to define and implement a policy that will protect your organization.
Meeting BYOD Security Risks and Challenges
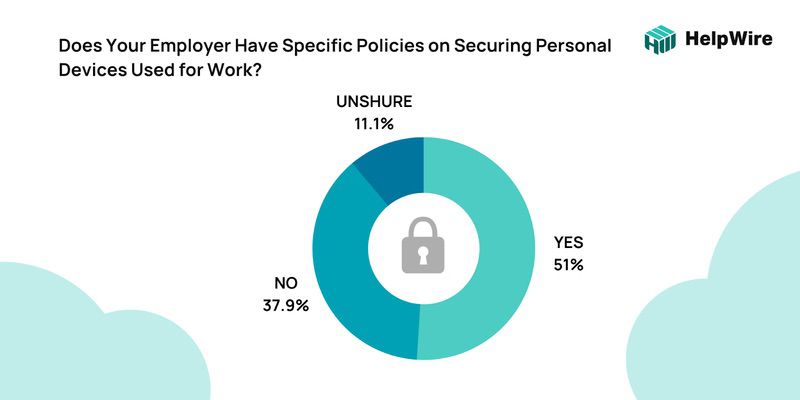
According to the research, despite the obvious security risk of not having a clear BYOD policy, just over half (51.0%) of respondents indicated their firms had specific BYOD regulations on safeguarding personal devices.
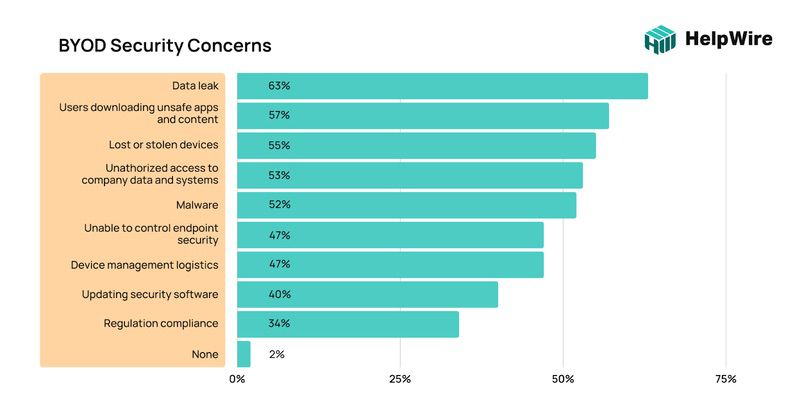
In addition, according to the data, 75% of employees use their cell phones for their jobs. This might result in significant BYOD risks and challenges for businesses. In any case, let’s take a look at the serious concerns associated with BYOD devices.
Source: Help Net Security, 2020
Device Infection
Mobile devices are easy targets for malware. Concerns about using BYOD are mostly related to security risks (company data leaks) and 52% of these risks are about malware infestation. Users often download applications, games and utilities without much thought to security. For example, the spread of malware through Google Play continued as well. In particular, the researchers found several mobile Trojan subscribers on Google’s official Android app marketplace in 2022.
According to the statistics, exploitation of popular game titles, where malware and unwanted software mimicked a pirated version of a game or game cheats, remained a popular mobile spread vector in 2022.
When using a laptop or desktop computer, it’s so easy to keep delaying security updates as it’s not convenient, but this is extremely risky. In a BYOD environment, it is important to ensure all devices are running the latest operating systems with the most recent updates applied.
Many personal devices are poorly protected by the free versions of antivirus software or not at all. Too often these provide a poor defense against cyber attacks.
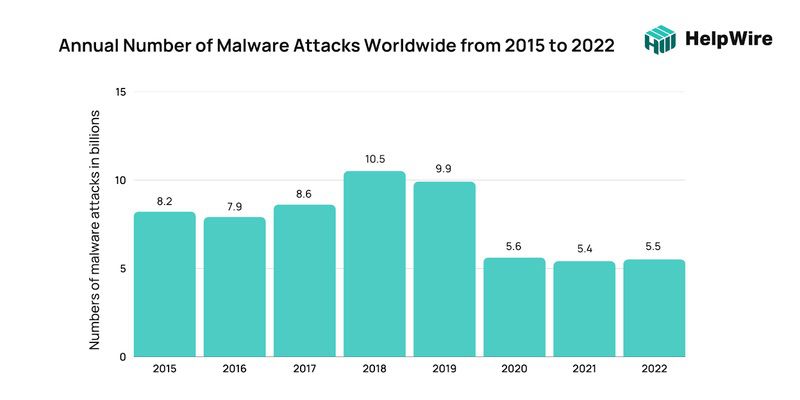
Data Leakage and Loss
According to 63% of businesses, the main security risk of BYOD is data loss or leakage. Whether your employee uses their personal device to access their mailbox or other business data, there is a risk for data leak and data loss.
In addition, malicious email links, which are three times more likely to be clicked on a mobile device, are claimed to be the origin of 91% of cybercrime. Therefore, these gadgets pose a serious threat to your organization. Once an attacker gains access to a device, they can:
- • Read and access all data on the device;
- • Abuse stored credentials to access otherwise unauthorized resources in the corporate network;
- • Attackers can download and delete all business data, holding companies hostage if they wish to retrieve their data;
According to T-Mobile, 41% of all data breaches might be linked to misplaced computers, tablets, and cell phones. Lost or stolen devices can pose a risk, especially if an employee does not have sufficient security to prevent unauthorized access to their mobile device. Albeit a hard fact to believe, a report by Remote Workforce Research shows that 10% of stolen gadgets are never recovered.
Jailbroken devices
Jailbreak is a term used to describe the intentional removal of restrictions on devices. The most common case of this is to bypass the limits imposed by service providers. While this may make the device more user-friendly for the individual, it poses increased risks for the organization.
According to estimates, 9% of all iPhones are jailbroken, and a similar percentage of Android devices are rooted, which can expose businesses to security threats. Moreover, few businesses have jailbreak detection mechanisms in place to safeguard their IT infrastructure.
Employee Privacy
It may be necessary for the company’s IT department to install software or configure a Mobile Device Management (MDM) system to protect corporate data. However, this poses another challenge as it may be seen as a violation of your employees’ privacy. Most employees would not give consent to any software that would track or monitor their usage of their own personal devices.
Unsecure networks
Attackers frequently target insecure internet networks in public places like airports and cafes. When employees connect to work via public WiFi, your company’s data is at risk. The data sent and received by their devices can be intercepted by hackers, who may then use this information to access your business networks.
Device incompatibility problems
The wide variety of hardware configurations and protocols makes BYOD hard to adopt since various operating systems exist. Employees use multiple devices while working, which makes assessing BYOD risks challenging. Furthermore, finding a universal security solution is difficult since each operating system has different network security choices..
How to Manage BYOD Security Risks
With the aid of a good BYOD policy and security strategy, BYOD hazards may be reduced, and business data utilized on personal devices can be protected. Here’s a closer look at some of the greatest challenges to adopting BYOD security and how businesses can solve them with the appropriate tools.
Define your BYOD policy
Companies that let employees use their mobile devices must establish a BYOD policy that gives proper instructions on using these devices. These policies safeguard companies from various security issues. Here are some elements that any successful BYOD policy should have:
Whitelisting
Outline the authorized applications, including social media platforms, email services, VPNs, and other cloud applications. Choose whether workers can install and use applications that pose a security or legal risk on the same device that will connect to your company’s network.
Devices
Indicate which devices and operating systems are permitted. For instance, some companies permit only Apple devices to be used. If using various custom devices is acceptable, each supported device should have its own security access.
Many device models and manufacturers are supported by the majority of mobile management suites. The BYOD program should not permit the use of devices that are not supported by the support matrix. Additionally, devices need to be updated often with the newest OS and bug fixes.
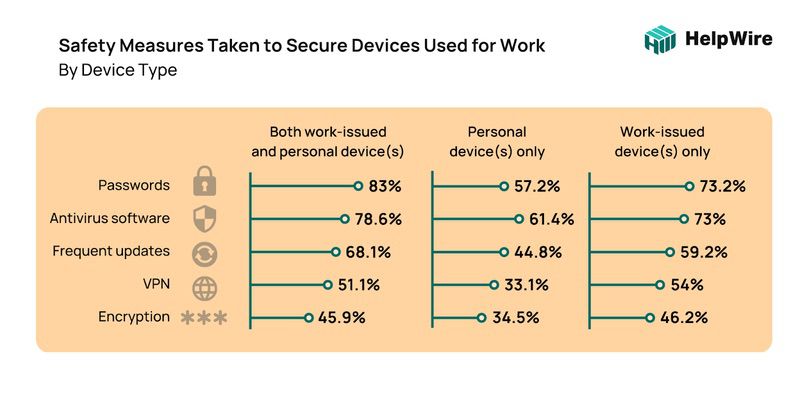
Passwords are still the most relied upon security measure for both work issued and personal devices. Personal devices tend to use Antivirus software more as their first line of defense at 61.4% over 57.2% for passwords. Encryption comes in last at around 45% for both work and personal devices.
Written BYOD policy
The BYOD security policy for each corporation will differ depending on the laws regulating your sector and business activities. Decide on your own rules and regulations, have everyone sign the BYOD policy, and let them know whenever there’s an update.
Give Superb IT Assistance to Remote Employees
For remote employees, effective IT assistance is essential. The remote assistance tool helps resolve technical issues quickly without disrupting work. Support teams can quickly troubleshoot and diagnose issues by forming remote connections, and providing immediate fixes.
The software’s remote control feature enables support staff to locate the underlying issue, provide speedy assistance, and gain access to the employee’s system. This prevents workers from having to explain intricately, resulting in quicker problem-solving.
What’s more, utilizing secure remote support software reduces the risk of unauthorized invasion by protecting data and controlling access.
By leveraging the on-demand remote desktop service HelpWire, companies can offer their employees efficient support, instantly resolving Mac and PC issues and thereby maintaining productivity.
Encryption for Data at Rest and in Transit
Due to the nature of BYOD it is imperative for all sensitive data to be encrypted. This applies to data storage and transit. Encryption serves as a safety net should your data land up in the wrong hands.
Strong passwords are not enough. Data must be encrypted for the entire lifecycle of the data, while at rest and in transit. All encryption keys should be under the management of the organization’s IT department.
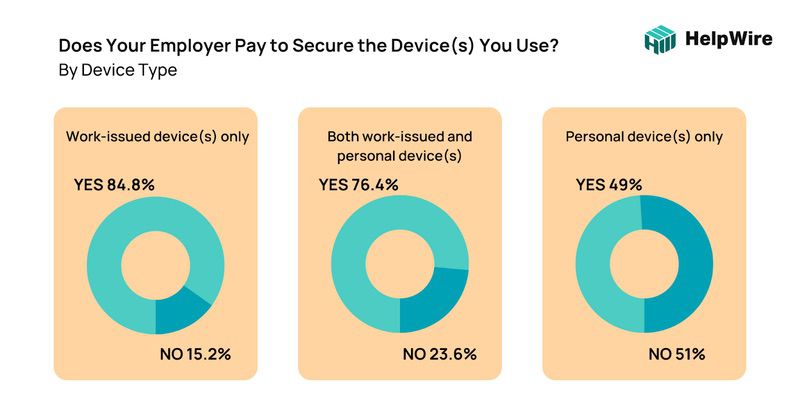
When asked whether companies spent money to secure both work issued and / or personal devices – 84.8% only secure work issue devices.
Containerization
Containerization is the packaging and segregation of a device into a safe bubble. Each “container” can be protected by a separate password with its own security policies. This allows the users to access their device without a risk of cross contamination and introducing security risks to the company’s network.
When accessing data or applications within a container, all other applications or parts of the device not included in the containerized area become inaccessible. Containerization offers the best of both worlds as the employee can still access their device, but personal apps are inaccessible during work hours.
Containerization doesn’t provide any security to the user’s personal data outside of the container.
Implement Mobile Device Management (MDM) Software Application
Mobile Device Management (MDM) software allows secure remote control over devices that are connected to the organization’s network. These devices include laptops, printers, smartphones and tablets.
MDM software is especially useful when a device is lost or stolen, as IT are able to remotely delete any confidential data, or even lock the device to render the hardware useless. According to reports, about 56% of BYOD companies utilize MDM and remote wipe to properly manage security.
Consider an Employee Exit Policy
When an employee leaves the company, there must be a process whereby all corporate data is removed from the employee’s personal devices. It is advisable to create exit protocols to ensure that this happens without compromising the employee’s own data or personal information. It is advisable to make a backup of all personal data before any removal process is initiated.
Educate Your Employees About Security
Many security breaches are as a result of human error. As such, it is of utmost importance to educate all staff members about the company’s BYOD security policy. It must be clear what each person may or may not do on their devices and why. In addition, repercussions must also be made clear at the onset.
All in all, BYOD has the potential to be very successful and bolster your business operations. These advantages include increased worker productivity, improved job satisfaction, and cost savings because you won’t need to purchase new equipment. Therefore, it is necessary to deal with any possible BYOD security risks.