Amazon WorkSpaces vs Azure Virtual Desktop: A Detailed Comparison
Virtual desktop infrastructures (VDIs) are an excellent solution to many of the challenges encountered by remote IT workers. Two popular offerings from the major cloud providers are Microsoft’s Azure Virtual Desktop (formerly Windows Virtual Desktop) and Amazon’s AWS WorkSpaces.
We are going to take a close look at the offerings of two major cloud providers. Our comparison of AWS WorkSpaces vs Azure Virtual Desktop will highlight the differences between the two solutions with an eye toward helping you find the product that meets your business objectives.
What is Azure WVD?
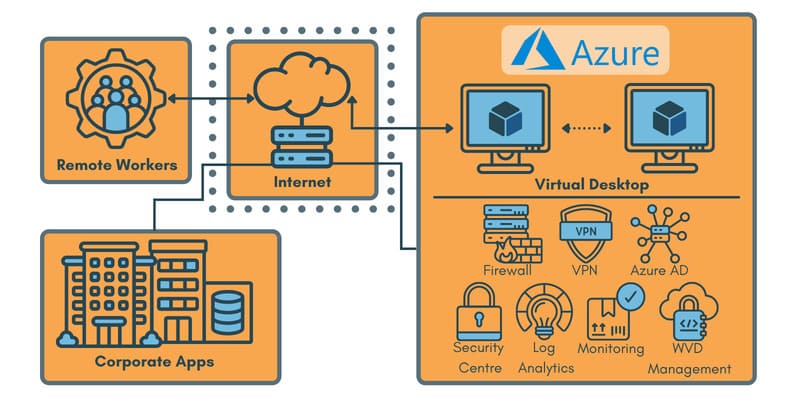
Azure Windows Virtual Desktop, also known as Azure WVD, is Microsoft’s cloud-based desktop virtualization offering. As with other services from Microsoft, this remote work solution is easily scalable and very secure. Azure workspaces can be set up quickly and offer a viable method of providing virtual desktops to any number of employees who are physically located anywhere in the world. Companies of any size can manage the rollout of Azure WVDs using the Azure portal. The virtual desktops are designed for running multiple Windows 10 sessions and support the Office 365 Pro-Plus Experience.
The features companies enjoy when implementing Azure Virtual Desktops include:
- • Microsoft’s intelligent security that ensures compliance and protects computing resources;
- • The ability to provide employees with Windows 10 desktops anywhere from any device;
- • The potential to scale and modify VDI deployment to address evolving business objectives;
- • Reducing the cost of existing Microsoft software licenses.
What is Amazon WorkSpaces?
Amazon WorkSpaces is Amazon Web Services’ cloud virtual desktop solution. Customers can choose to implement virtual Microsoft Windows or Amazon Linux desktops. It only takes a few minutes to provision a new virtual desktop instance using either operating system. AWS helps simplify the delivery of virtual desktops to employees by reducing the complexity of managing VDIs, operating systems, and hardware resources. Amazon WorkSpaces can be engaged on an hourly or monthly basis to meet the needs of any company.
The features that are available to Amazon Workplace customers include:
- • Use of the customer’s applications and software licenses on the virtual desktops;
- • Persistent desktops that promote enhanced productivity;
- • Consistency in the tools used to manage virtual WorkSpaces and physical desktops;
- • Control over which IP addresses can access a virtual workspace;
- • Data encryption at rest with AWS Key Management Service;
- • Multi-factor authentication for improved security.
Comparing Azure Virtual Desktop vs AWS WorkSpaces
Azure Virtual Desktop and Amazon WorkSpaces are both viable options for companies implementing remote desktops for their employees. Teams using either platform can access the applications and desktops they need regardless of the time of day or their location. The two services, however, are not identical and the differences in certain areas can be substantial. Let’s take a look at some of the ways these two services differ and the specific features they offer.
Features
An obvious difference when comparing AWS WorkSpaces vs Azure Virtual Desktop is the operating systems available for the virtual environment. Where Azure only supports the Windows OS, AWS WorkSpaces can run Windows or Linux. This can be a major factor when determining which solution works best for a prospective client.
The following table summarizes Amazon WorkSpaces vs Azure WVDs in some specific ways. As you can see, the two products offer very similar general feature sets.
Feature | AWS WorkSpaces | Azure Virtual Desktop |
Operating system support | Windows and Linux | Windows |
Third-party integrations | A variety of solutions: see below | Mostly Microsoft-focused: see below |
Security | Encryption and multi-factor authentication | Encryption and multi-factor authentication |
Backup and Recovery | Data is synced every 24 hours | Default policy backs up data once per day |
Remote access | Desktop as a service | Desktop as a service |
User management | Single sign-on, policy management, user provisioning | Single sign-on, policy management, user provisioning |
Integration
Both AWS and Microsoft offer their customers integrations with additional software products and applications that increase the value of their virtual desktops. The specific integrations may make a difference when choosing between the two solutions. Here’s a breakdown of how Azure VDI vs AWS WorkSpaces stack up with integrations.
Azure Virtual Desktops offers integration with:
- • LiquidWare;
- • AdminStudio;
- • AuthPoint;
- • Automatic Robotic Process Automation;
- • Azure Security Center;
- • Microsoft 365;
- • Microsoft Azure;
- • SysTrack.
AWS WorkSpaces integrations include:
- • LiquidWare;
- • AWS Directory Service;
- • Amazon Web Services (AWS);
- • FortiSandbox;
- • Rocketbot;
- • TeamViewer Remote Management;
- • TeamViewer Frontline;
- • TeamViewer Tensor;
- • Servicecamp.
Deployment
The deployment methodology is different for the two virtual desktop solutions. Companies opting for Azure Virtual Desktops are getting a rollout of virtual Windows machines tightly integrated with Microsoft software. This makes Azure VDIs a logical choice for companies that rely heavily on Microsoft products.
AWS WorkSpaces provide an example of a software as a service (SaaS) solution built around virtual desktops. Users can go with either a Windows or Linux OS and choose from among the multiple integrations to augment their systems. Customers can also use their software tools and applications with AWS WorkSpaces.
Pricing
In the world of corporate IT, the cost of a service or product is necessarily taken into account when choosing between alternative options. Any comparison of AWS WorkSpaces vs Azure WVD would be incomplete without taking a look at the pricing schemes available for customers of these remote work solutions. It can be a complicated task to effectively project the price of a virtual desktop initiative.
In general, customers may be able to save some money by going with AWS unless they are heavily invested in Microsoft software licenses. Microsoft-centric companies may find it more economically beneficial to go with Azure WVDs.
AWS WorkSpaces Pricing
Amazon WorkSpaces does not require customers to make a large capital investment to get started. Users can be billed either hourly or monthly with costs based on the specific software bundles and the number of active WorkSpaces.
Hourly billing
Customers pay a flat monthly charge that covers storage and infrastructure resources for each workspace. Ongoing use of the WorkSpaces is billed hourly. This payment plan is appropriate for use by part-time workers or short-term usage scenarios.
Bundle prices vary according to the AWS region in which a customer resides. For example, hourly prices in the US East regions range from $0.09 to $1.19 per hour with the flat monthly infrastructure fees running between $5.80 and $15.20 per user per month.
Monthly billing
Customers whose primary desktop is Amazon WorkSpaces will benefit financially from the monthly billing option. It comes at a fixed monthly rate that includes unlimited usage of the workspace. Rates range from $16.80 to $108.80 per month based on the specific resources the customer uses.
All plans provide additional storage billed at $0.10/GB. For $15 per month, customers can access an application bundle that includes Trend Micro security, Microsoft Office Professional Plus, and other software utilities.
Prospective customers should consult Amazon for the latest prices for Amazon WorkSpaces. The company also offers the Amazon WorkSpaces Cost Optimizer that helps organizations find the most effective and efficient way to use WorkSpaces.
Azure Virtual Desktop pricing
Two factors need to be considered when calculating the pricing for Azure Virtual Desktop implementations. They are:
User access rights – These costs include license entitlement which may be eliminated if customers have eligible Microsoft products. There is also a per-user cost for access to Azure Virtual Desktops.
Azure infrastructure costs – These costs vary based on the selected infrastructure components. Among the specific infrastructure elements in scope are virtual machines, storage, and networking capabilities.
Azure Virtual Desktops are available for free trials. A complete overview of Azure VDI pricing can be found on this Microsoft support page.
Device and Desktop as a Service
Amazon has been a leader in developing cloud solutions like Desktop as a Service (DaaS) since 2006. Other major vendors like Microsoft and Google have made inroads, but AWS still leads the pack. Its portfolio of services is more extensive than those of its competitors and includes tools for system admins, developers, resource management, and mobile access.
The range of services available with AWS can be a major selling point for virtual desktop customers. Companies that want more flexibility in their DaaS solution should take a close look at what Amazon has to offer. Organizations that primarily use Microsoft software may find that Azure VDIs offer a smooth transition to the world of virtual desktops.
Performance and Reliability
The performance and reliability of a virtual desktop solution is important when choosing a vendor. There is some slight lag that is noticeable with both AWS WorkSpaces and Azure Virtual Desktop when you are launching programs or apps. The delay was slightly less intrusive when using Azure’s product.
As far as reliability, organizations that want a solid service level agreement (SLA) that defines the minimum uptime should look at Amazon’s offering. Microsoft does not provide an SLA, though they strive for 99.9% availability. Amazon offers a 99.9% uptime SLA that includes financial penalties if they cannot meet the promised availability.
What is a Virtual Desktop?
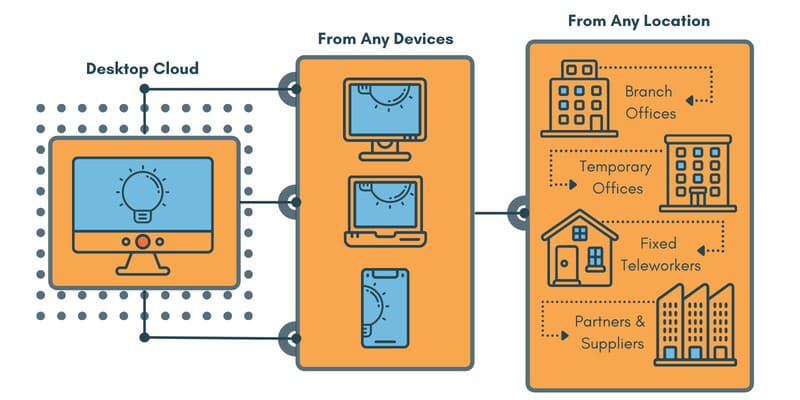
A virtual desktop is a computing environment where an operating system and other applications are virtually encapsulated in a comprehensive software package that is run as an instance on local or remotely located physical hardware. Connecting to the virtual desktop gives a user the same functionality as if they were sitting in front of the physical system.
Virtual desktops can be hosted using an organization’s on-premises physical infrastructure. Products like VMware have long been used to implement virtual WorkSpaces. An alternative is to take advantage of the infrastructure available through cloud providers. Cloud computing brings benefits such as enhanced security and virtually limitless and easy scalability that can be hard to replicate in a business’s terrestrial data center.
Conclusion
Virtual desktops have become an essential component of many organizations’ IT strategies. Going virtual can be a big step for a business and identifying the right solution can be challenging. Companies looking at Azure WVD vs AWS WorkSpaces will find that both providers offer viable methods to address the needs of a mobile and remote workforce. A careful review of the offerings will help customers decide which solution is best suited to meet their business objectives.