Remote Desktop Group Policy Management
- HelpWire
- →
- Blog
- →
- Definitive Guide to using Microsoft Remote Desktop
- →
- How to remotely enable RDP
- →
- Enable RDP via Group Policy
If you want to set up RDP on multiple computers in the same domain, your best bet is to enable RDP group policy. The remote group policy management tools available to IT administrators on Windows Server have a complete GUI and do not require any complicated terminal commands.
Rights to Enable Remote Desktop GPO
In order to adjust group policies in your domain, you need to have domain administrator rights. This can be verified by running the “whoami” command. You can add the /all argument to display more information.
In PowerShell, you can check your domain by looking at environmental variables. This can be done by running “$env:UserDomain”.
Necessary Group Policy: Allow Remote Desktop
All of the following are under Computer Configuration > Policies.
The most basic policy is to allow RDP sessions in the first place – a host-side option, so you don’t need to enable it on clients:
Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections > Allow users to connect remotely using Remote Desktop Services
However, it’s not the only option you’ll need. A firewall rule is likely required, if you want the PCs to be accessible on public networks:
Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security > Inbound Rules
There, you can create an exception for the TCP port that Remote Desktop uses on given PCs. The default port for RDP is port 3389, but it can be changed.
Finally, enable RDP access for a user group by going to:
Windows Settings > Security Settings > Restricted Groups
Add the group to Restricted Groups and set it to be a member of Remote Desktop Users.
How to Enable RDP GPO
Once you’ve selected the necessary policies for RDP, it’s time to edit them.
-
Use the Search Bar to find the Group Policy Editor.
-
Locate the domain you want to edit. Right-click it and select “Create GPO in this domain…”.
-
Open the selected domain and navigate to any required policies, enabling them.
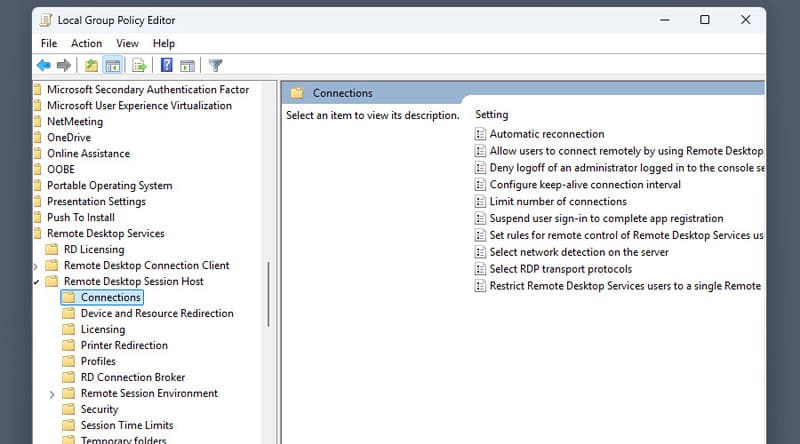
-
Run “gpupdate /force” in a CMD prompt with administrator rights.
Optional Policies
It’s dangerous to allow unauthorized access to your computer over RDP. The following policy enables user authentication and adds an extra obstacle for malicious actors:
Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Security > Require user authentication for remote connections by using Network Level Authentication
There is a number of useful RDP policies under Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host. After navigating to the folder, you can set the following:
– Redirect Local Devices – this affects USB devices, such as USB drives and webcams;
– Session Timeouts – disconnecting an inactive session after a time is a security measure, to avoid someone walking in and taking over while the remote user is AFK;
– Session Compression & Graphics Quality – also configurable clientside, but can be enabled as a default setting;
– Limit Concurrent Sessions – more useful on multi-user systems with limited resources, to avoid overload.
Start Remote Sessions without GPO - HelpWire

Are you looking for an easier way to host or connect to remote sessions? HelpWire is a simple, feature-rich remote access service. The Standard version of HelpWire is free both for personal and commercial use.
Starting a session with HelpWire doesn’t require you to have a static IP or a domain administrator role. It’s also completely unnecessary to enable RDP GPO – simply download, share the connection link with the client, and it’s done. In addition to this, HelpWire has many features that make it perfect for remote support:
-
Complete session security
-
Drag-and-drop file transfers
-
Compatibility with multi-monitor desktops
-
Built-in client-host chat
-
Image quality settings
-
Team management