What is Remote Desktop Services: Full Guide
In this article, we will take a detailed look at Microsoft Remote Desktop Services (RDS). We will discuss the various components that make up Microsoft RDS and how RDS can be used to implement a remote desktop session or access cloud-based applications. Remote desktop services are incorporated into the Microsoft Windows operating system, making them available to a large user community.
Many organizations make use of remote desktop services to address the needs of their distributed workforces. With a remote desktop connection provided by RDS, end users can access Windows desktops down the hall or on the other side of the globe from their familiar personal computer.
What is RDS?
Microsoft Remote Desktop Services is a set of components of the Windows operating system that serves a distinct purpose. It combines several features that enable users to access graphical desktops and Windows applications remotely.
The remote capabilities that eventually became RDS were initially called Terminal Services in Windows Server 2008 and prior versions of the OS. As the product evolved to RDS from the terminal server, more functionality was built into the product. In many cases, the terms RDS and terminal server are used interchangeably.
RDS is primarily targeted at business users as evidenced by its lack of support to connect with machines running Windows 7 Starter or Home, Windows 8 Home, Windows 8.1 Home, or Windows 10 Home editions. Despite being a Microsoft-centric remote access solution, remote desktop clients for macOS, Android, and iOS devices are available at the Microsoft store.
What are the uses of RDS?
Organizations use RDS in two specific ways to access Windows desktops and applications remotely and help meet business requirements.
- • The RemoteApp facility of RDS enables a business to make cloud-based applications available to users on personal computers or mobile devices. This enables application management to be centralized and ensures consistency throughout an organization.
- • The Microsoft Remote Desktop component of RDS lets users connect to alternate desktops from their current device. After establishing the connection, users can interact with the remote desktop according to the permissions they have on the system. Individuals can use this new virtual desktop as if it was installed on their physical machine.
We will take a closer look at Remote Desktop and RemoteApp shortly.
The benefits of RDS
The benefits of RDS are closely tied to its business uses. Following are the benefits businesses can expect to enjoy when implementing a remote desktop services environment.
- • Windows applications can be delivered to devices lacking the capabilities to run them natively. This includes machines with inadequate resources as well as those running alternative operating systems like iOS or Android.
- • More computing resources can be supplied to centralized, cloud-based applications that are used remotely to provide enhanced performance rather than upgrading all end-user devices.
- • Data can be stored in the cloud, keeping it more secure in the event of a user device failing or being stolen.
- • The time required to configure new user devices is reduced by delivering apps and desktops from a master image in the cloud to a device that supports a remote desktop client.
These benefits add up to a more streamlined method of managing and delivering applications to end-users, saving the business money on technical administrative resources. Employee productivity is raised by the ability to remotely access desktops and applications. As an organization’s remote workforce grows, these benefits become more valuable.
RDS Windows Server components
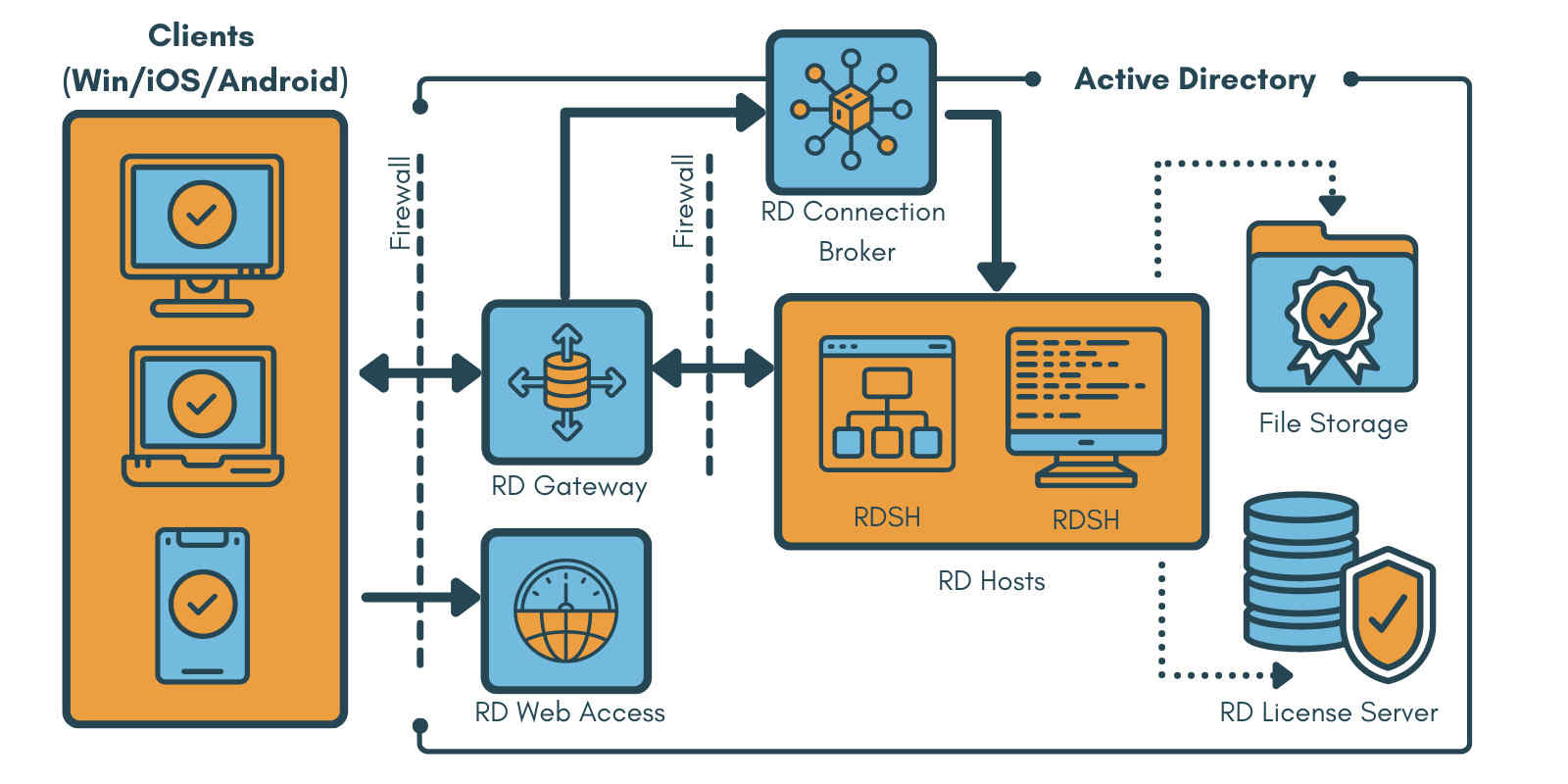
RDS is comprised of multiple Windows Server components that each fulfill a designated role.
Remote Desktop Services Host (RDSH) – The RDSH stores the apps and desktops that are shared with users. These items can be organized into collections using multiple RDSH servers and customized to control access to specific apps and desktops.
Remote Desktop Connection Broker – The connection broker serves as the desktop services manager, supervising the incoming remote desktop connection requests made to RDSH server farms. It acts as a server manager and can load balance requests across multiple RDSH servers.
Remote Desktop Gateway – The RD Gateway grants access to users on public networks to Windows apps and desktops hosted in Microsoft Azure’s cloud services.
Remote Desktop Web Access – RD Web Access allows users to access applications and desktops through a web portal and runs them using their device’s Microsoft Remote Desktop client application.
Remote Desktop Licensing servers – RD Licensing servers are required in an RDS environment. We will discuss the issues of remote desktop licensing in a later section.
RemoteApp
RemoteApp is the facility within RDS that allows applications to be delivered to remote users from the same server regardless of the operating system on their device. Users access Windows apps as if they were installed on their device, while in reality, they are running on a remote server. Applications are centrally managed to ensure consistency throughout an organization’s remote user community.
Remote Desktop
With Remote Desktop, users obtain access to a complete virtual Windows desktop that can be accessed from any device using the compatible Remote Desktop client. This facility enables an end-user to access a Windows desktop and associated apps from their smartphone or tablet.
RDS Licensing
Microsoft RDS is a licensed product that requires users to have an RDS CAL (client access license). The remote desktop license lets users access Windows Server published resources like apps, files, and desktops.
An RD license server is used to install and track the RDS CALS. This tracking method enables organizations to pay based on capacity and usage. As more users or devices access centralized resources, more CALS need to be purchased. Newer RDS CALS can access older RDS Host machines but old CALS cannot access new hosts. New licenses will need to be purchased to work with new RDSH servers.
No license is required to use RDS functionality during a grace period that lasts for 120 days. After the grace period has expired, a valid RDS CAL is required before users can access an RDSH server.
Understanding RDP, VDI & RDS

There is often some confusion around the differences in the terms remote desktop protocol (RDP), remote desktop services (RDS), and virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI). Let’s clear up any misunderstanding by taking a closer look and comparing these related three-letter acronyms (TLAs).
RDS vs VDI
RDS and VDI are two methods of providing remote users with access to applications and virtual desktops that exhibit the following differences.
- • VDI is built around the Windows Client operating system while the foundation of RDS is Windows Server.
- • When using VDI, the end-user machine can be running any operating system where RDS requires them to run Windows.
- • VDI enables multiple users to connect to a virtual machine or operating system. In RDS, users share the OS, applications, and hardware resources of the host when connecting to a remote desktop session.
- • RDS employs a single server to enable access by users over a network using the Remote Desktop Protocol. In VDI, users get individual virtual instances hosted on VDI virtual machines.
RDS vs DaaS
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) is an offering from public cloud providers that makes it possible to run a desktop environment on a virtual machine. Though a DaaS solution provides similar functionality to Microsoft’s RDS service, it exhibits the following differences in how it implements a virtual desktop.
- • The virtual desktops provided by a DaaS solution do not require a host machine running Windows Server.
- • In a DaaS environment, each hosted desktop can be implemented in an isolated virtual machine. This provides enhanced security over an RDS host that services multiple desktops.
- • A DaaS environment is more scalable than when using RDS, as customers are not limited by the resources available on the Windows Server host machine.
- • No dedicated remote desktop gateway such as a VPN is necessary with a DaaS solution. Users can access their remote desktop through a standard web browser.
RDS vs RDP
RDS enables users to connect to Windows machines that support Microsoft’s remote desktop protocol (RDP). RDP is not a remote solution in itself but is used to enable communication between remote clients and servers. Other remote software solutions support RDP and enable users to access Windows machines from distant locations. Due to the popularity of Windows, RDP is a very popular communication protocol.