Internet of Things & Telecom — How IoT Impacts The Telecom Industry
After a long time spent witnessing OTT (over-the-top) companies cannibalize their revenue opportunities, the telecom industry is jumping at the chance to regain its footing. How is this possible?
The trend of incorporating IoT into the telecom industry allows for building services based on outstanding connectivity.
IoT in the telecom industry is shining a light on numerous unique and valuable revenue-building opportunities. This shift is inspiring savvy telecom operators to develop new strategies and implement the power of digital into their business.
To reassume their top position, communication service providers venture into the IoT market, which experts expect to bring in more than $1.5 trillion annually by 2030.
According to recent trends, one out of four huge organizations trades data on formal online data marketplaces. Telecom companies, specifically, can take advantage of possibly capitalizing on their access to the massive collection of data accumulated through their infrastructure.
Opportunities & Meaning of IoT to Telecom Service Providers
The constant growth of people living a constant digital lifestyle greatly multiplies the demand for connected devices. As it stands, the global volume of this demand already exceeds 13 billion devices.
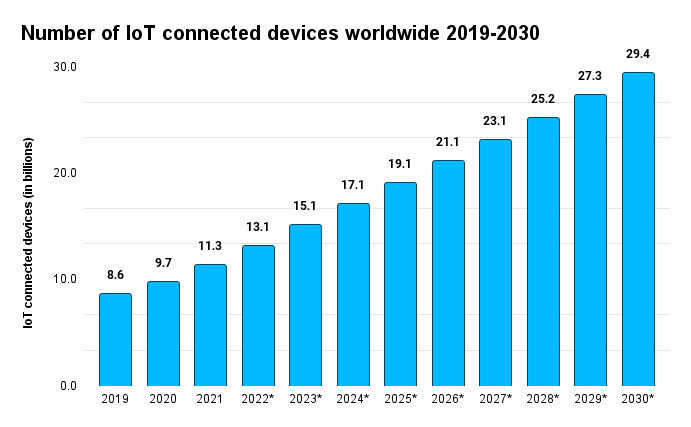
The growth statistics, predictions, and society’s constant urge to automate processes, all contribute to businesses implementing smart solutions into their infrastructure.
All of this gives telecom businesses the advantage over their competition since they have both the skills and resources to connect and control/manage the IoT devices using their network.
Most telecom companies already participate quite actively in this space, providing their sensors, devices, network connectivity, and IoT applications to build newer and better value-added services.
Primary IoT Use Cases in Telecom
The evolution of the Internet of Things in telecom lets these organizations monetize their data and extend their businesses to serve other industries providing customers with services that support more than just network connectivity. Adversely, service providers themselves, won’t have the chance to establish themselves as IoT leaders.
Communications service providers (CSPs) can venture toward new and exciting possibilities, and by working with other IoT-centered organizations, businesses can develop more services based on their unique elements.
IoT examples in telecom include data analytics, intelligent networks, billing, IoT platforms, CRM, and cloud services — and service in a variety of sectors like healthcare and manufacturing.
Industrial Monitoring Systems

A startling 87% of industrial businesses intend to grow their integration of IoT to proactively manage equipment and resources in real-time. Industry 4.0 creates incredible and vast opportunities for telecoms to transition into manufacturing, via powering connectivity within intelligent supply chains.
One IoT capitalization method for CSPs is by offering specially-tailored network offers. These companies can unite all elements of the complicated ecosystem of the manufacturing industry.
This could range anywhere from flow meters to temperature sensors — which allow for the benefit of improved production efficiency, end-to-end supply chain visibility, and mitigating expenses.
One of the first telecom pioneers to take advantage of IoT in telecom was T-mobile. The carrier company launched the US’s first narrowband IoT network in 2018. This was meant to support their industrial clients in utilizing the power of data within their warehouses.
Smart Cities and Shared Economy

Narrowband IoT and 5G stand as the primary means of smart city implementation. This allows CSPs to surmise the value of mutually beneficial public-private partnership agreements with municipalities, local governments, and educational institutions. Allowing them to provide crucial services revolving around digitizing and integrating urban infrastructure.
Telecoms can assume numerous roles within the smart-city value chain that maximize their revenue share and help develop efficient, inclusive and connected environments.
Along with offering broadband, operators have the option of expanding their ability to provide monitoring solutions, and data management — as well as create branded customer-facing service delivery platforms.
Smart Homes and Buildings

Thanks to IoT, telcos also play a major role in the steadily growing smart home and building market. Telecom companies can provide bandwidth and network resources that connect utilities (like heating and air conditioning), and security elements (like locks, cameras, alarms, and appliances), allowing them to position their business as a third-party reseller for tailored consumer apps and services for this sector.
One of the first telecom companies that fueled smart home investments was Comcast, which expanded its home entertainment portfolio with the addition of XFINITy — a service combining TV, internet, mobile, voice, and home management into one convenient dashboard.
Nowadays, more and more telecom organizations follow Comcast’s example.
Seeking to monetize smart home opportunities, many brands travel the partnership route, collaborating with software and hardware vendors to create connected home solutions. Such examples include Telefónica Spain’s partnership with Microsoft where they’re crafting new AI-powered, in-home experiences for customers.
Another example is Verizon’s collaboration with Honeywell, an effort that allows them to embed the provider’s LTE connectivity into smart meters.
Telecom IoT for the Healthcare Sector

The most notable use cases of telecom IoT exist in remote healthcare. This involves providing remote healthcare diagnostics solutions and devices, remote asset management platforms, and smart incident management systems.
Telecom operators can build robust, secure, and reliable networks that interconnect smart apps and devices. Simultaneously, their business partners manage the software and hardware infrastructure.
Because of data sensitivity and increasingly sophisticated tech advancements, IoT deployment in the medical field demands large investment contributions. However, the impacts on society thanks to these implementations are incredibly beneficial.
South Korea supplies one particularly intriguing example, involving its telecom operator, SK Telecom, which signed a strategic deal with Yonsei University to create an IoT-driven hospital that lets patients control their own lighting, entertainment options, and hospital beds.
Additionally, numerous leading medical facilities in China are collaborating on the implementation of the first 5G-based hospital network standard, which will optimize healthcare delivery throughout the country.
Autonomous Driving and Connected Vehicles

The automotive industry has a significant share in the IoT endpoints and 5G industry because telecoms remain dominant as providers of the core components of autonomous vehicle ecosystems.
The results greatly enhance vehicles with optimized telematics, automation, infotainment, navigation, and fleet management solutions.
Nokia is enhancing autonomous driving with its Worldwide IoT Network Grid (WING). This managed service offers OEMs that provide a multi-tenant, cloud-native IoT core infrastructure and management platform.
On top of offering secure and reliable managed connectivity services, CSPs invest resources into their own connected car services — which simultaneously extend high-end in-vehicle entertainment and out-of-vehicle experiences.
How Telcos Themselves Use IoT

CSPs also venture forward on IoT telecom journeys of their own by using the power of acquired data to tap into their inner workings and obtain valuable insight. Telecom companies implement complex software platforms as means of connecting a multitude of physical assets, as well as leveraging their combined knowledge to fuel decision-making and create prediction models.
On the inside, telecoms use IoT technology to add efficiency and optimization that benefit resources within their organization. One example is how, in just one year, AT&T was able to optimize energy use in its facilities by 9M kWh by harnessing IoT-enabled building energy management. This resulted in savings of nearly one million USD.
IoT Meaning for Telecom: The Future of Value-Added Services
Telecom companies often find themselves at a turning point after establishing their ability to provide customers with reliability and connectivity. Being that the profitability and scope of traditional telecom services plateaued, CSPs have to expand on foundational strengths.
These strengths include a well-optimized telecommunications infrastructure, impressive data sets, and 5G-enabled connectivity. All of this is necessary if they want to develop new and exciting value-added offers that put them on top of the communications value chain.
The issue is that when telecom companies only attempt to outwit competition — this won’t be a (long-term) effective method for any particular telecom organization.
IoT offers a variety of valuable opportunities for telecoms to outshine OTTs and thrive in the new, cross-industry territory. However, providers must establish an ecosystem of trustworthy and innovative technology partners to take advantage of these opportunities.
After all, only by building and nurturing partnerships with high-quality software and platform organizations can CSPs open the door to sustainable growth and new revenue streams thanks to modern IoT services.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can IoT Be Used in Telecom?
What Are the Main Telecom IoT Protocols?
NB-IoT is used more often in Europe and is mainly devoted to low-cost and low-bandwidth data connections.
LTE-M is more frequently used in North America, developed with a focus on mobile connections and (comparatively) higher bandwidths.
How Can the Telecom Industry Benefit From IoT?
- • Higher speed and expanded bandwidth: IoT protocols and 5G network integration help ensure data transmission from thousands of devices to multiple users, while preserving bandwidth and communication speed at scale.
- • Low latency: The technology mitigates downtime, which is vital for customers that have business services that rely on real-time processes.
- • Increased power efficiency: Telecom companies can greatly improve power efficiency with the addition of IoT technologies, making them more capable of managing millions of connected devices.
- • Increased revenues: By providing IoT services and solutions, telecommunications companies can better retain clients, acquire new ones, and generally improve customer loyalty. From a commercial standpoint, this ensures added income growth and fuels long-term revenue.