IoT Smart City, a Complete Guide
Role of IoT in Smart City Concept
Everything is changing right before our eyes. Smart cities are taking these changes and turning them into solutions.
It is now possible to use your devices beyond their typical functions like social media, messaging, photography, and data storage. Think barely having to use paper money or keep receipts, never having to bring physical credit cards or IDs, or spending less and less excess fuel or precious physical energy all because of a handy internet-connected device.
IoT allows objects to connect and transmit data to each other through the internet. These systems use that data to make the best possible decision for a given activity or task, whether it is tasked to be accomplished by an individual or a big company.
Smart cities use IoT-based wireless technologies and a cloud-based system to process real-time data from objects placed all around the town. The digital ecosystem formed between these objects enables the city to exhaust fewer resources, conserve energy, and help the environment.
Smart City Technologies

IoT reaches further into our lives than we think.
Seemingly mundane activities can be made more efficient and more environment-friendly with IoT ideas for smart cities, which helps navigate the constant problems arising from urbanization.
Smart city IoT applications have solutions for traffic, waste management, weather and climate change, persons with disabilities, and many more. This is made possible by processing data between the source and the cloud, otherwise known as fog computing.
The following are examples of the most common technologies that are used in smart cities:
Smart Utility Meters
Energy spending takes up much of the expenses of every company, making IoT use in energy management a financial necessity.
Smart utility meters that are placed directly in buildings allow the tracking of the flow of energy used by an establishment. We’re talking billions of dollars saved by 2035 solely due to the adoption of smart utility meters in the US.
Smart Transportation
Vehicles are becoming increasingly connected, with nearly all vehicles in the US predicted to be using smart transit options in less than 20 years.
Smart transit mostly consists of GPS services and voice search (or a combination of both) IoT functions that increase the safety of drivers and passengers by enabling hands-free navigation guidance.
These available services are only the beginning of more smart transit options.
Smart Grids
Smart grids allow residents of a city to store energy with their own battery units and solar panels.
These are used during peak hours to lessen energy consumption from the same source. Such is especially useful during hours of the day with the highest energy consumption like the early to late evening.
With the city’s smart grid, city-wide energy conservation is made possible. Amsterdam is one of the remarkable cities implementing a battery-grid system to save energy.
Smart Waste Management Solutions
Smart waste bins improve segregation, garbage pick-up schedule and routes, and even contribute to traffic decongestion.
IoT developments in waste management, such as the EvoEco, provide interactive features to its users. It communicates the financial benefits of recycling and guides households in segregating their everyday waste. Simultaneously, the EvoEco transmits data to companies about appropriate times for pick-up depending on the amount of garbage collected.
Smart Air Quality Monitors
The effect of indoor air quality (IAQ) on an individual’s and a community’s health is often underestimated.
To maintain constant vigilance in such environmental conditions even though citizens are indoors, smart air quality monitors carefully analyze air pollutants.
They detect different particles and substances present in the air and send real-time information alerts to easy-access devices such as smartphones and other portable devices.
All these make managing an exponentially growing population much more efficient than traditional means.
Sensors, smart appliances, and wearable Bluetooth devices all fall under IoT. Given the right data and software, such technologies in smart cities can function to protect the environment and provide easier transport options. It can also increase safety amid environmental hazards and damage to infrastructure and guide with day-to-day home and office tasks.
IoT-based smart city solutions are the epitome of social responsibility in rapid technological development.
Smart City Examples
The world is expected to have a population of 9.8 billion by 2050, with a majority of these people living in cities and megacities. Evidently, urbanization is showing no signs of slowing down.
As technology shapes the reality of different places around the world, internet of things (IoT) technologies gain more and more relevance as novel and sustainable instruments that are helping people live fuller and fuller lives. Some of the most well-known cities around the world, like Singapore and London, have already benefited from IoT, with the promise of even more groundbreaking uses in the future.
Here are some cities that are already at the forefront of keeping up with these rapid changes using smart city IoT solutions:
Singapore
The famous island city-state of Southeast Asia has been named the smartest city in the world in 2021.
Described as a hyperconnected city, SG boasts of robust connections between government officials, researchers, businessmen, and residents to proactively provide the utmost benefit of IoT to the country as possible.
Initiatives are geared toward making Singapore a Smart Nation. This nation adapts to the unique characteristics of its population over time with the use of smart technologies supported by IoT.
Singapore’s population as of 2022 is 5.64 million and around 25% of these people are expected to be above 65 years old by 2030, making healthcare innovations a necessary investment for the aging and frail population.
The pandemic called for even more developments in this field of IoT. IoT applications in healthcare include the use of sensors in monitoring devices and patient wearables. There are also call alert systems and emergency detectors for frail persons living alone or isolated due to infectious diseases.
London
Also named one of the smartest cities in the world, London shows unmatched ambition in the field of smart mobility and cleantech.
With concrete goals dating 20 years into the future, London aims to use IoT to develop public services that respond to problems specific to the citizens of London and its visitors.
Transport strategies are of particular interest as London aims to provide publicly accessible transportation methods to most of the population by the year 2041. As the city has been supporting contactless payments for their public transportation for more than a decade, it is easy to trust just what they can do given more time.
For instance, lamp posts that make use of IoT are being tested as a potential multifunction smart device. Smart lamp posts can transmit data on traffic, historical sites, and air quality.
The latter supports London’s advocacy for cleantech, or technology that studies and alleviates pollution and climate change.
Seoul
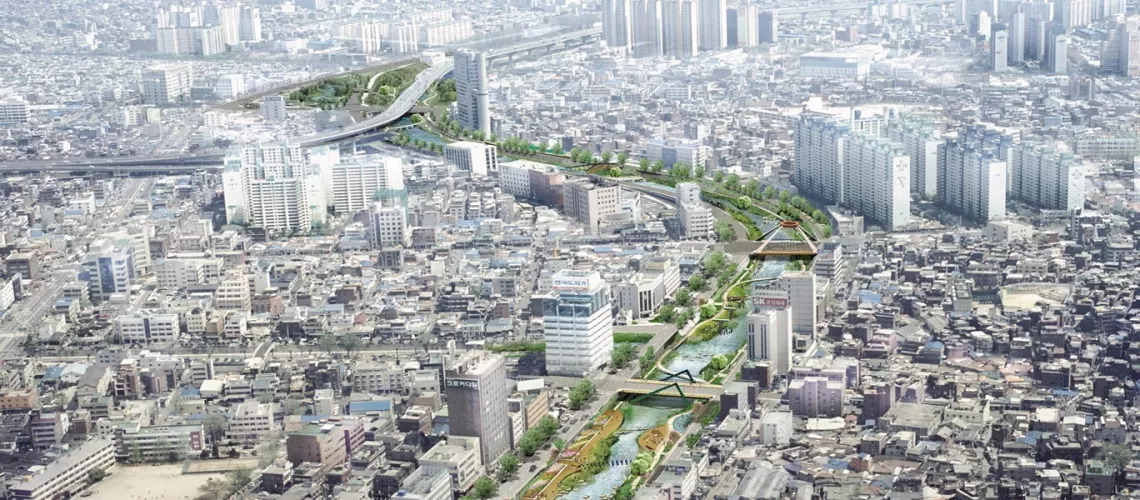

Image Credit: Seoul Metropolitan Government
The heart of the Korean Peninsula, Seoul, has long been known to have one of the fastest internet connections in the world. With this, it just seems like the perfect place to harness IoT.
Amidst continuing success in the tourism and pop culture scene, another one of Seoul’s claims to fame has definitely been its early dive into the use of smart technology. Being the home of some of the most famous smartphones, Seoul has been using IoT in public transport and warning systems when other localities were still in the early stages of planning their own smart cities.
The local government’s commitment to developing citizens’ digital literacy is commendable, with lectures and free classes being offered to individuals who are low-income and are least likely to use new technology, such as the elderly. Seoul’s emphasis on citizen-focused interventions and their subsequent success simply prove that smart citizens make a smart city.
New York City
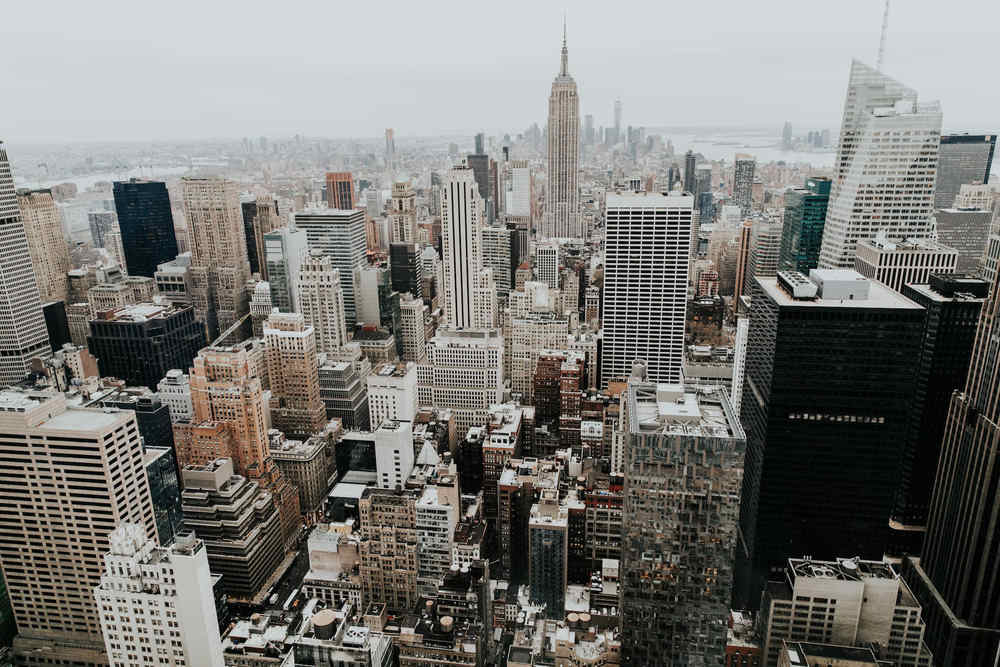

Image Credit: Hannah Busing, Unsplash
New York City (NYC) is famous for a myriad of things: musical theater, skyscrapers, and the concrete jungle within which its rising population bustles every day. But its smart technologies also deserve recognition.
As one of the most populated megacities, energy usage, water consumption, and carbon emissions inevitably rise as more and more people migrate to this world-renowned destination.
With IoT-based smart city solutions such as automated water meters and air quality monitors, the city of New York is set on reducing its carbon emissions to zero by the year 2050.
Startups that can access open data compete in yearly competitions to establish more environmental and social solutions for the citizens of New York City, attracting economic investments and providing job opportunities.
Barcelona
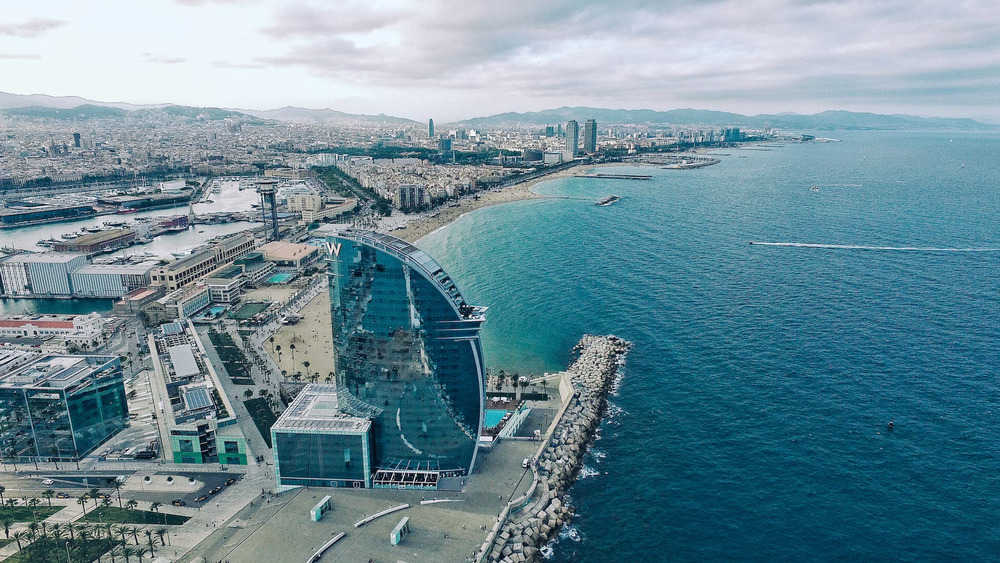

Image Credit: Benjamín Gremler, Unsplash
The city of Barcelona is, quite literally, connected by a 500-kilometer fiber-optic cable that runs throughout the city. This provides services such as citywide WiFi among many other public utilities made possible by this 30-year IoT smart city project.
Waste management is one of the key sectors made more efficient by IoT as the city implements sensor-equipped waste bins that collect household garbage, and detect the amount and composition of garbage and whether toxic materials are present. Detection is followed by appropriate action that the IoT technology deems best.
Digital bus stops and vehicle-sharing applications further enrich the daily smart city life and create cultural and environment-friendly experiences that inspire citizens to trust and cooperate with new innovations.
Copenhagen
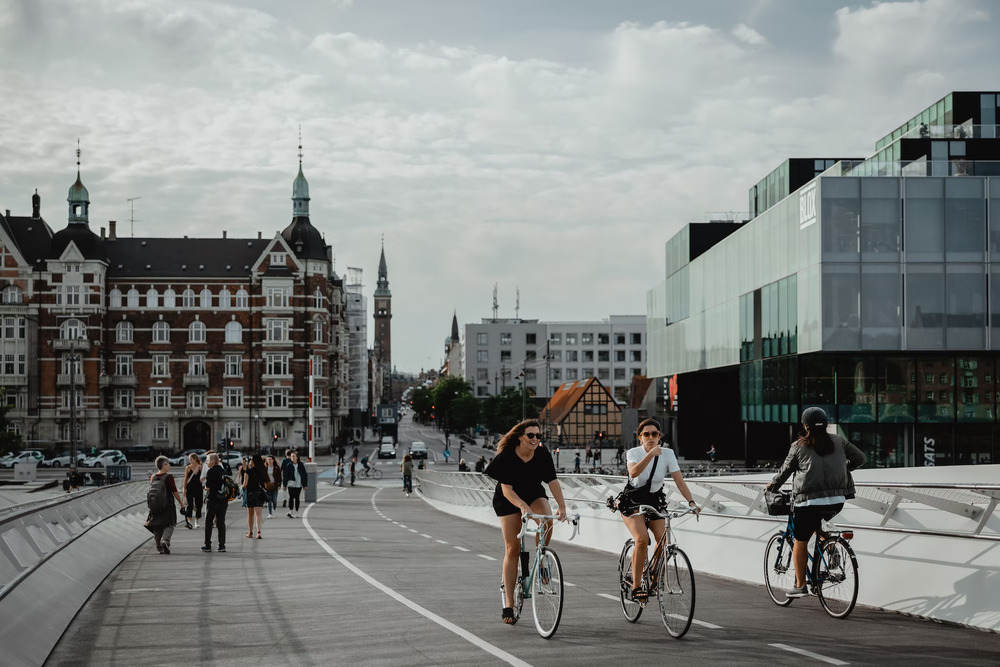

Image Credit: Febiyanr, Unsplash
The capital of Denmark is making a name for itself as a growing tourist destination and a city that is firmly dedicated to reducing its carbon emissions.
Partnership projects initiated by the local government through the Danish Outdoor Lighting Lab (DOLL) provide IoT solutions focused on lighting and environmental sensing. Copenhagen thoroughly monitors its carbon emissions to control its pollution sources accordingly through outdoor laboratories.
They also enhance the tourist experience through digital services that connect visitors to needed data and devices while they travel within the city.
Shanghai

Image Credit: Henry Chen, Unsplash
In Shanghai, China’s booming financial center, IoT efforts are being made to digitize government services, lessen paper use, and relieve traffic congestion.
The Citizen Cloud application is a versatile platform where residents can process government requests for official documents such as birth and marriage certificates, legal papers, healthcare coverage, and many more.
In Shanghai’s side of the world, social inclusion and accessibility are the centers of smart city development.
Statistics: What Does it Take to Make a Smart City?
Physical and human resource investments are essential for a smart city to thrive and keep thriving.
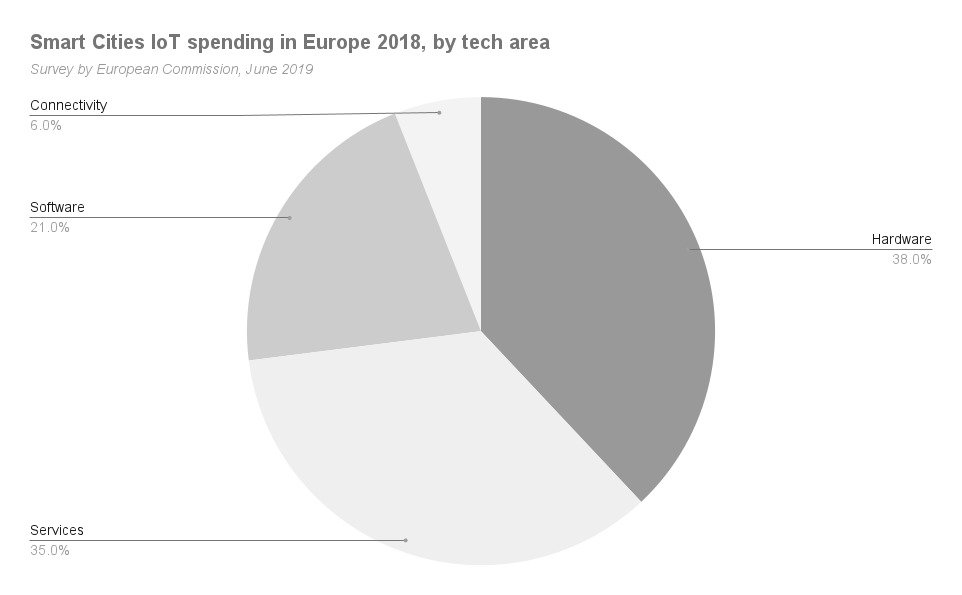
Analytics by the European Commission in 2018 show that hardware and services take up the two biggest costs in the creation and maintenance of IoT solutions in smart cities, with 38% and 35%, respectively. Meanwhile, software and connectivity take the lesser fractions, with 21% and 6%, respectively.
Such data can give smart cities or developing smart cities ideas for proper funding and allocations as they start building their digital ecosystems to alter the town as they know it, and for the better.
Beyond the Numbers
City governments play arguably the biggest role in the development of smart cities.
People and establishments cannot comfortably adopt these promising devices and software without appropriate policies. Partnerships between sectors can enable legislation that allows the appropriate balance of data sharing, data security, investment, and income.
Aside from legislation, a city’s capability to adopt new technologies lies in trust and harmonious relationships between providers, officials, and citizens.
Smart Leadership in Smart Cities
So many IoT solutions are in place, already bettering the quality of life for many of us. And still so much is being developed. More and more cities are gearing up for the next era of technology in the form of IoT, with the best interest of people and the environment in mind. What else is missing?
Making smart cities possible takes more than just creating the devices and enabling end-to-end connections. It requires commitment and cooperation from different sectors of the community.
As promising as it may sound, new technologies are bound to face challenges, especially as data is openly shared across borders. IoT-based smart cities are not an exception. When done right, however, the IoT smart city projects are a win-win for everybody, including you.
IoT opens gateways of new opportunities for local and national economies by attracting investment, income, and many new jobs, but only when smart leadership values smart citizens as much as they value data analytics and smart technologies.
Local governments must treat stakeholder and citizen support as important assets because IoT is definitely here to stay. IoT is the future.