10 Examples of IoT in Healthcare
IoT medical devices are one of the fastest-growing niches within the IoT market. Wearable devices—specifically IoT healthcare devices—are crucial detection and emergency sensors that help protect people tracking their medication, or those struggling with health problems like diabetes and asthma.
Examples of IoT in healthcare can often be wearables functioning with Bluetooth and companion apps on a smartphone. Such technologies provide healthcare professionals with crucial insight that results in better healthcare.
But defining how IoMT impacts IoT security (and why healthcare IoT devices must be managed effectively), scenarios where IoT devices are implemented must be understood.
In this article, we’ll discuss ten IoT healthcare use cases, and how these devices influence IoT security.
1. Remote Health Monitoring
The most frequently implemented use for IoT medical devices is remote patient monitoring. IoT healthcare devices automatically log physical health metrics like blood pressure, heart rate, body temperature, and more—all without the patient needing to be anywhere near a healthcare facility.
These devices provide numerous opportunities for healthcare professionals and hospitals to monitor patients—but it also gives patients the freedom to track their health independently. Additionally, the many styles of wearable IoT devices offer many benefits (like fitness tracking),and hurdles.
IoT in healthcare has all but eliminated the necessity for patients to travel back and forth to medical offices because patients can easily collect the data themselves.
IoT medical devices track and transmit patient health insight to software applications that healthcare providers (and/or their patients) can easily review.
Note: Optional/integrated algorithms analyze the data and allow it to recommend treatments, or generate emergency alerts. Such add-ons can have a significant impact on a patient’s health and wellness outcomes (like an IoT sensor that detects an abnormally low heart rate in a patient.)
In such a scenario, the device may generate an alert that offers healthcare professionals an opportunity to provide remote medical support.
One considerable hardship regarding remote patient monitoring devices is ensuring a patient’s sensitive data is private and secure when collected by these IoT devices.
Useful tip: In the healthcare sector, ensuring secure and confidential remote medical support is essential. Adopting HelpWire for IT support in healthcare environments becomes a key approach to offer secure remote medical help. HelpWire supports healthcare practitioners with software setup and problem-solving. This enables medical facilities to uphold superior patient care standards while complying with privacy and security guidelines.
2. Glucose Monitoring
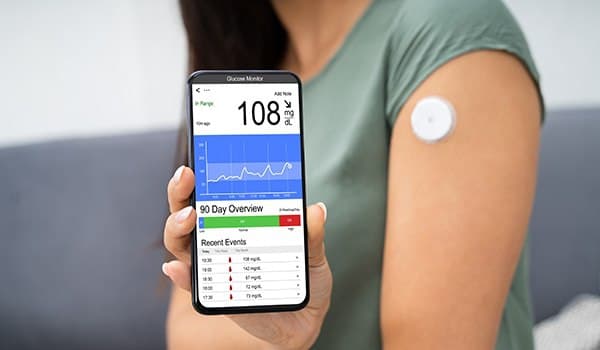
Accurate and timely glucose monitoring is notoriously challenging for the over 30,000,000 Americans living with diabetes. Monitoring and manually recording glucose levels are not just inconvenient, but manually entered glucose levels are only recorded during the moment a test gets administered.
For those struggling with unpredictable glucose level fluctuations, periodic testing isn’t a reliable method to detect problems.
IoT healthcare devices offer solutions to these issues with continuous and automatic glucose level monitoring. This monitoring device eliminates manual record-keeping and can alert patients when their glucose levels are not where they should be.
The current issues facing those designing IoT healthcare devices for glucose monitoring are:
- • Developing a device small enough to monitor continuously without disrupting patients’ day-to-day lives.
- • Developing IoT medical devices that won’t require frequent recharging.
The good news is, these challenges aren’t untenable, and devices addressing these issues are sure to revolutionize how patients manage glucose monitoring.
3. Portable Heart Rate Monitoring
Heart rate monitoring can incur many of the same challenges as glucose monitoring—this is true even if a patient is stationed within a medical facility— and routine heart rate monitoring can’t defend against rapid heart rate fluctuations.
Hospital-specific, traditional cardiac IoT medical devices require patients to remain physically connected to wired machines, which has a degenerative impact on mobility and quality of life.
Thanks to advances in IoT technologies, numerous portable heart rate monitoring IoT healthcare devices are widely available. These developments allow patients to move freely, while continuously monitoring their heart rates.
While hyper-accurate results are still challenging, most modern devices provide accuracy rates of at least 90%.
4. Hand Hygiene Standarts
Up to now, there hasn’t been an effective method for ensuring providers and patients within healthcare facilities wash their hands properly. Since appropriate hand-washing measures are critical in minimizing the risk of spreading contagions, this is a serious issue.
But nowadays, numerous hospitals and medical facilities implement IoT devices that remind people to sanitize their hands when entering hospital rooms. Such devices even offer instructions on the most effective sanitization methods to mitigate specific risks for specific patients.
One drawback is that these devices can only remind people to clean their hands—not do it for them. But research reports that IoT sanitization monitoring devices can reduce infection rates by over 60% in hospital environments.
5. Mental Health Monitoring

Insight into depression symptoms and a patient’s overall mental health are additional metrics that used to be difficult to track continuously. Healthcare professionals may consistently ask patients how they’re feeling, but can’t fully anticipate sudden changes in mood or emotional wellness. Frequently, and unfortunately, patients also don’t always accurately report their feelings.
“Mood-aware” IoT healthcare solutions address these problems by tracking and analyzing heart rate and blood pressure data. Additionally, insight gleaned from IoT medical devices infer information regarding a patient’s mental health, and advanced mood-monitoring IoT devices can even monitor eye-movement data.
The biggest challenge with mood-monitoring devices rests on how metrics gained can’t predict symptoms of depression (or other causes for concern) with 100% accuracy. But this same challenge is also present in in-person mental assessments.
6. Parkinson’s Disease
To treat Parkinson’s patients effectively, medical professionals must have the ability to measure how symptom severity fluctuates throughout a patient’s day.
An IoT medical device/sensor promises to make such tasks easier by continuously collecting Parkinson’s symptom data. Simultaneously, IoT healthcare devices provide patients with the freedom to live their lives independently instead of being forced to spend excessive time in medical facilities for observation.
7. Connected Inhalers

Medical conditions like COPD and asthma usually involve attacks that can happen suddenly and with almost no warning. IoT-connected inhalers help protect patients by monitoring the frequency of attacks, and recording environmental data that helps healthcare professionals recognize what triggers an attack.
Additionally, IoT-connected inhalers can alert patients if/when they’ve forgotten their inhalers at home, noting that they’re at higher risk of suffering from an attack because their inhaler isn’t present (or when inhalers are misused.)
8. Ingestible IoT Sensors
Recording data from within the human body is commonly intrusive, disruptive—and can get messy. The simple fact is, no one wants a camera/probe inserted into their digestive tract (as an example.)
IoT medical devices designed to be ingestible sensors can track and record critical insight from numerous physiological systems within the body (in a far less invasive method.) Ingestible IoT healthcare devices can track PH levels in the stomach, or help pinpoint the source of internal bleeding (as just examples of IoT in healthcare scenarios like this.)
Obviously, ingestible devices must be small enough to easily swallow and dissolve or pass through the human body effectively on their own. As a result, numerous IoT medical device brands are racing to develop ingestible sensors that meet these requirements.
9. IoT-Connected Contact Lenses
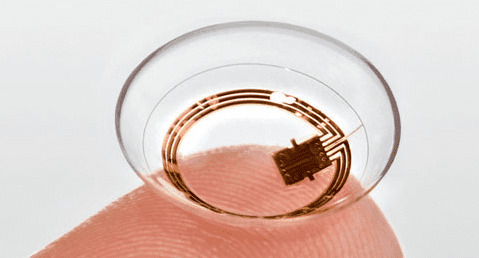
“Smart” contact lenses offer additional opportunities to acquire medical data in a non-intrusive way. Such wearable devices can also encompass micro-cameras that let wearers take pictures with their eyes, which is likely why entities like Google have patented connected contact lenses.
Whether used to improve health results or otherwise, “smart lenses” promise to transform the human eye into a powerful tool for digital interactions.
10. Robotic Surgeries
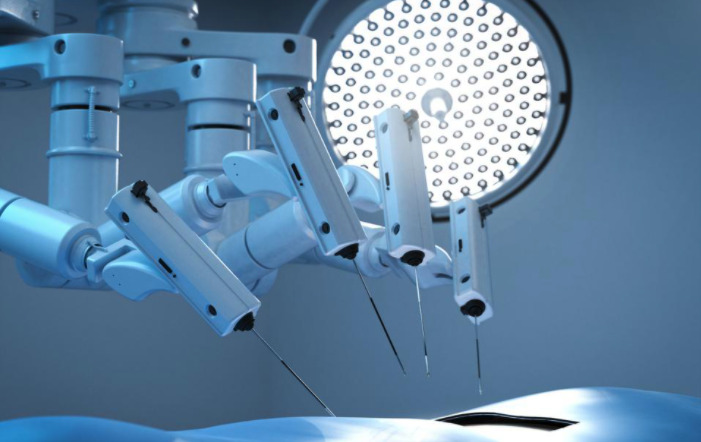

Surgeons can more effectively perform complicated procedures (those that would be otherwise difficult using the human hand) by injecting IoT medical devices (like tiny internet-connected robots) into a patient’s body.
Simultaneously, robotic surgeries performed by miniature IoT healthcare devices can reduce incision sizes usually necessary from traditional surgery. Smaller incision sizes contribute to a less invasive process, and lower healing times for patients.
Such devices must be small and reliable enough to perform surgeries with as little disruption to the patient/process as possible—and must be able to interpret complex conditions within bodies to formulate effective decisions regarding how to proceed during a surgery.
However, IoT robots are already used in multiple surgeries, demonstrating that the challenges mentioned above are conquerable.
The Trends of IoT in Healthcare
Projected size of the Internet of Medical Things worldwide (from 2016 to 2025)
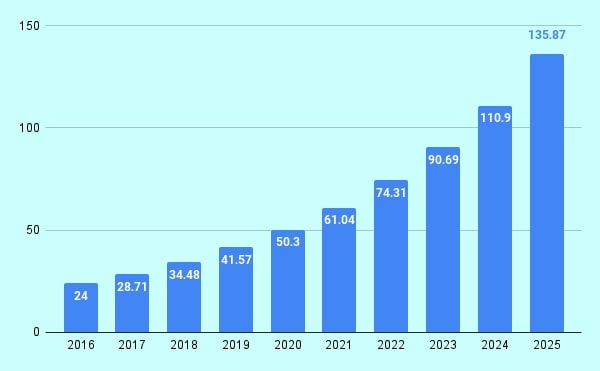
This statistic outlines the projected volume of the Internet of Things in healthcare (IoT) within the global healthcare market (ranging from 2016 to 2025.) In 2016, medical-related IoT revenues amounted to 24 billion U.S. dollars globally, with forecasts predicting an increase well beyond 135 billion US dollars by the year 2025.
What Are the Benefits of IoT in Healthcare?
The plethora of benefits of IoT in healthcare are vast and diverse:
- • Increased comfort and convenience for patients improve patient satisfaction and expedite recovery;
- • IoT healthcare devices, wearables, and data tracking let medical professionals monitor patients with greater precision—meaning they can offer more-informed treatment options;
- • IoT security systems improve safety for patients and medical staff;
- • UV light sanitation systems help spaces remain clean and help prevent the spread of disease/infections.
An additional advantage of IoT healthcare solutions is future-proofing. While the initial investment is required for implementing IoT infrastructures (installing devices, training staff members, etc), ROI will show a steady increase over time.
Once IoT ecosystems are established, integrating new IoMT devices (as developed) becomes much easier. As a result, IoT-enabled “smart hospitals” will edge out competing facilities that don’t implement IoT healthcare solutions.
What Are the Challenges of Implementing IoT in Healthcare?
While many advantages exist regarding IoT technology for healthcare, there are hurdles to overcome. Therefore, healthcare facilities should understand and acknowledge potential challenges when adding IoT in healthcare environments.
1. Security
Hospitals and other healthcare facilities must observe strict security standards around patient privacy and compliance guidelines. In addition, healthcare organizations— especially massive healthcare networks— must oversee security for multiple facilities and large repositories of data.
Implementing IoT devices into healthcare environments can improve security management, and automated security software is an easy method to protect healthcare staff and patients.
Power over Ethernet (PoE), Nexos primary protocol, is an exceptionally secure solution, making it an ideal option for healthcare facilities observing high-security protocols. Learn more about Power over Ethernet.
2. Adoption
Adopting a new IoT framework is a massive obstacle in healthcare. Migrating an entire facility to new systems and procedures takes time, and upfront costs and installation time are a significant barrier for many organizations —especially small medical facilities or more rural clinics.
All in all, the advantages of IoT in healthcare vastly exceed the cons around initial time and cost investments. IoT healthcare ecosystems lead to higher-quality care, cost-savings, streamlined processes, and much more.
3. Integration
Integration feels quite overwhelming with the vast number of device types and protocols. To experience the maximum efficacy of IoT medical devices, they must seamlessly connect and be easily automated and controlled. Without a robust and intuitive IoT platform, IoT-specific devices can falter.
Igor’s PoE-enabled IoT solution was developed to function with multiple systems and unite them into one platform. This provides users with a simple and effective experience condensed into and a single dashboard where users can manage every device within the IoT ecosystem.
4. Data Collection
Data collection is a massive IoT healthcare challenge. However, it also offers massive enhancement opportunities. IoT systems produce a great deal of data, so prior to implementing IoT medical ecosystems, discuss the system’s design and priorities revolving around data tracking and usage.
Once these priorities and possibilities and outlined, it’s easier to integrate IoT ecosystems that generate actionable data reports.
Additionally, there are many options on how to use this data to enhance the overall patient/healthcare experience.
Why Is Security So Important for IoT in Healthcare
Critical security obstacles must be resolved before the efficacy of IoT medical devices can be maximized.
Beyond all else, IoT-related professionals (like developers, healthcare providers, and managers) must effectively secure all data collected by IoT devices. Most of the collected insight from these IoT medical devices qualifies as protected health information under HIPAA (and other relevant)regulations.
This means IoT devices run the risk of being used like gateways for data thieves (82% of healthcare entities report attacks against their IoT healthcare devices.)
Developing secure IoT hardware and software is just one means of resolving these security challenges. However, ensuring all IoT devices effectively defend against data-hacks is just as important.
Patient monitoring devices with older software/firmware versions (or devices improperly decommissioned) offer hacking opportunities into network, or data theft.