TOP-13 Remote Desktop Clients for Linux – Linux RDP Client Comparison
- HelpWire
- →
- Blog
- →
- Access Linux Desktop From Windows
- →
- Remote Desktop Client For Linux
Most users will encounter situations when they will require a remote desktop access client for Linux to control more than just a single application or program. That’s when a Linux Remote Desktop client like AnyDesk, NoMachine, X2Go, Zoho Assist, and some others we’ll discuss below becomes incredibly valuable. Implementing these tools allows users to access and control a remote computer from a plethora of devices. Numerous protocols exist, but many users will be familiar with SSH.
Linux RDP client to Windows machine
For example, tech support professionals using Linux operating systems might need to direct someone through a remote software installation or reconfigure settings remotely on a Windows machine.
Even though Secure Shell doesn’t provide remote desktop connection capabilities, this Linux remote desktop client does allow users to install the software needed to enable secure access to remote operating systems.
To begin, use your Windows machine to select Windows PowerShell (from the Power Menu), and hit enter.
ssh [IP_ADDRESS]
Accept the certificate, then enter the correct username and password. A connection is now established.
The methods described above work for all Debian systems including Fedora. Such compatibility doesn’t exist because the OS provides built-in support for remote tools.

Be sure to set up the remote access features on the physical machine running Ubuntu (initially), and installation of any additional tools won’t be necessary.
If you are looking for additional software, keep reading our TOP list. We collected all remote access clients for Linux, which work the best.
1. Remmina
Remmina remote desktop client for Linux desktops ranks fairly well as far as performance, offering the flexibility to edit connection quality whenever the user wants. The remote client supports an extensive protocol list allowing users to enable remote connections with various systems.
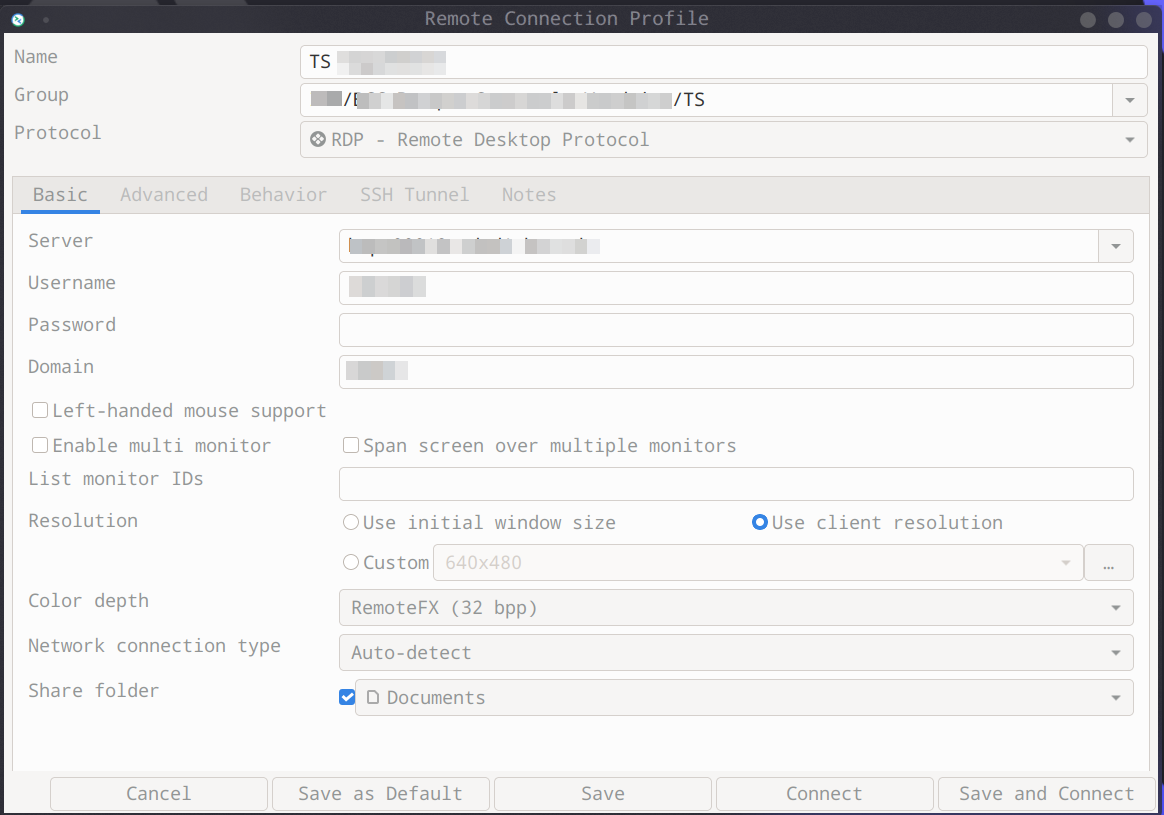
While this client lacks server software of its own, it’s great for connecting with numerous remote servers. Unfortunately, it doesn’t offer some of the additional functionality that competing Linux Mint remote desktop clients provide.
Remmina is a popular choice for establishing remote desktop sessions on Linux computers. It’s an open-source solution written in GTK+ and distributed under the GNU GPL license. One of its best features is its intuitive and user-friendly interface that streamlines its use. The interface is similar to web browsers with tabs to manage multiple session windows. You can connect to Windows and Linux machines simultaneously using a tab for each session.
2. rdesktop
rdesktop is one of the open-source RDP apps (much like TightVNC). It’s a UNIX client used for connecting with Windows Remote Desktop Services. rdesktop can communicate natively with Remote Desktop Protocol to display the user’s Windows desktop.
Not only was rdesktop the first remote access tool that works great as a Kali Linux remote desktop client, but also it was the most frequently used client for many years. However, as of November 2019, the client is in search of new maintainers.
3. Xrdp
This client offers a graphical login to remote machines via the Microsoft Remote Desktop Protocol. No matter which operating systems you are using (i.a. Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android,) the Xrdp server tool can connect using various clients such as AnyDesk, TeamViewer, FreeRDP, NeutrinoRDP, rdesktop, Zoho Assist, and Microsoft Remote Desktop Client.
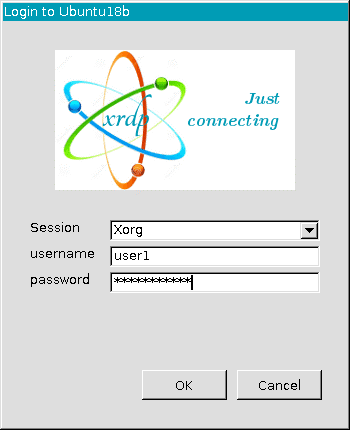
Using the server requires a simple setup, allows for port forwarding, and makes remote session access convenient and practical thanks to its compatibility with a wide variety of other clients.
4. NoMachine
NoMachine is an open-source remote desktop client for Linux that uses the NX technology protocol over VNC or XDMCP. It’s secure, fast, and very user-friendly and makes its way onto this list thanks to its user volume.
This Linux Windows remote desktop client’s popularity is usually attributed to its speed and ease of use, permitting users to access any remote device in a few clicks. The NX protocol supported its development, and what sets NX protocol apart is its high local speed. This speed provides a responsive experience that feels just like it would if the remote user were physically using the remote server’s desktop directly.
Offering secure encryption and reliability, it makes a fantastic personal server. Users can access practically all files (video, audio, document, etc.) Users can even share pretty much anything via its remote desktop client.
5. Chrome Remote Desktop
Chrome Remote Desktop is a free tool developed by Google that’s cross-compatible with any operating system/platform because it functions via a Chrome browser. This makes CRD a great remote desktop connection Linux client. Chrome Remote Desktop offers unlimited remote support, online meeting capabilities, and easy file access.
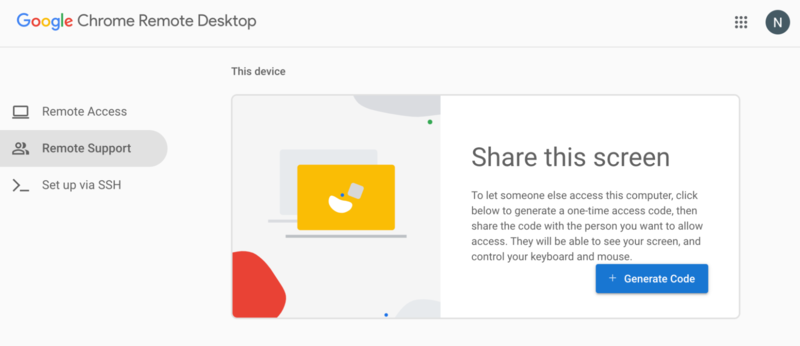
Chrome Remote Desktop is a popular option for personal use but does not furnish the same functionality for business use as apps like Zoho Assist or AnyDesk. Primarily, Chrome Remote Desktop is an add-on for Google’s Chrome browser. You need to have Chrome installed to use the tool. When using Chrome Remote Desktop, the remote device you wish to connect to has to already be up and running and have Chrome installed.
6. TigerVNC
This app is an open-source tool for a remote desktop client for Kali, and it’s completely free. Being cross-compatible with any operating system and offering excellent performance, the tool has two applications, the Server and the Client, enabling remote access to a remote computer using a GUI (Graphical User Interface).
The functionality of this app (be it for server or client) is distinctive as a standalone virtual desktop that allows each independent session to be launched via its configuration. It should be noted that this tool doesn’t operate like the alternative server that connects directly to the runtime desktop, for example, Vino or VNCx.
TigerVNC provides connection options that include choosing encoding levels, compression levels, and screen colors. You can share your clipboard with the remote session, interact with the session’s screen or just view it if that’s all you need.
The tool listens to port 5900 by default and has extensions for implementing advanced authentication. TLS encryption is used to protect traffic between the client and the VNC server.
As you can see, finding the right remote desktop client for Ubuntu Linux can open up a vast sea of options, and Tiger offers a wide variety of those.
7. Real VNC
Real VNC is a beloved remote desktop Linux tool for a plethora of reasons. From its fully encrypted desktop software, strong security protocols, and it’s user-friendliness, Real VNC is an excellent option for Linux users. Here are a few other noteworthy features:
- • Intuitive and very responsive
- • Offers exception stream speeds
- • Incredible audio and image quality
- • Multi-factor authentification
- • End-to-end encryption
- • Multiplatform access
- • 256-bit AES
Real VNC offers a ton of flexibility, giving users the option to watch screens in real-time—or take total control of a remote machine located anywhere across the globe.
8. Apache Guacamole
Another exceptional option is Apache Guacamole. This Linux-compatible remote desktop tool offers many convenient features and compatibility, making it a great clientless remote desktop tool.
- • Doesn’t require client software or plugins (just an HTML5 web app)
- • Free
- • Open-source
- • Supports many standard protocols (like VNC, RDP, and SSH)
The browser functionality of Apache Guacamole means that users can enjoy remote access from any device—regardless of where they are in the world.
9. FreeNX
With a core library by NoMachine and completely open-source, FreeNX comes in as an excellent remote desktop Linux option to consider. With a range of valuable and versatile features, we’ve outlined just a few of our favorites below:
- • SSH-based server/client system
- • Fast
- • Flexible
- • open-source
The only downside to this tool is, at the time of writing this article, the website link for FreeNX isn’t functioning. However, that’s a minor issue that we’ve resolved by sharing links to the distro-specific web pages!
10. Xpra
A reliable and multi-platform remote display and client forwarding remote desktop option, Xpra is an easy tool for forwarding desktop screens, applications, and so much more.
- • Access to individual apps or a full desktop
- • Open-source
- • Easily connect and disconnect from programs
Users can also disconnect and reconnect programs without losing their place/state in the program, from any machine. Via MS Windows, Mac OS X, or X11 servers, Xpra can also forward complete desktops.
11. X2Go
X2Go is a Remote Desktop solution primarily used to remotely access Linux machines. You might see this type of software called Remote Control. X2Go is an alternative to the Microsoft Remote Desktop Protocol.
X2Go is a responsive and secure method of accessing remote Linux computers. The remote computer you connect to is known as the X2Go Server. The Linux RDP client is installed on your computer and is used to access and control applications or the desktop on the remote machine. The Linux X2Go client can also be used to connect to a remote Windows computer.
The X2Go server component starts and manages the remote session on the remote computer. When you use the Linux remote desktop client, you are provided with a cloud desktop that has the benefits of a system that is always online, accessible remotely, easily scalable, and operates on a fast network.
The following tutorial demonstrates how to create an Ubuntu 20.04 XFCE desktop environment that can be accessed remotely using X2Go. The resulting cloud-based desktop furnishes the same utilities and functionality of a Ubuntu 20.04 and XFCE environment running on your local machine.
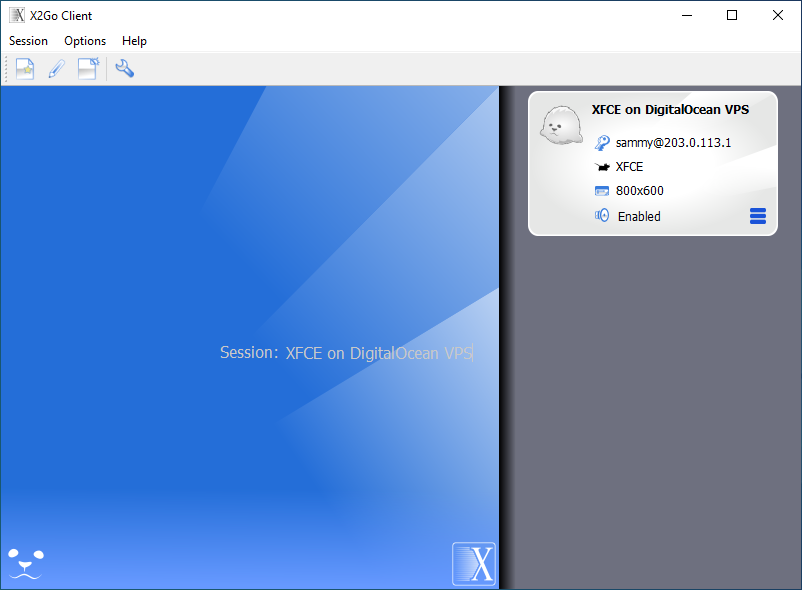
X2Go works well as an RDP client for Linux right out of the box. The solution is also very customizable, allowing you to configure your RDP Linux client to suit your needs and preferences. One option is to use keyboard shortcuts that can improve the user experience on both Linux and Windows systems. You can find additional information about customizing your session at X2Go’s website.
There are two methods of ending a remote session and closing any graphical programs currently running in it. The first technique has you log off remotely from the XFCE start menu. This method offers a clean shutdown but may leave some programs such as the session manager running in the remote computer.
The second method simply requires you to click the button in the bottom-right corner of the X2Go screen that is marked with a circle and a small line (like a power/standby icon). This option closes everything but may force close processes that don’t terminate cleanly. Before closing a session with either method, you should always save your work.
12. ZOHO Assist for Linux
Zoho Assist is a popular solution for establishing Ubuntu remote desktop clients from any location with an Internet connection. Remote support technicians favor Zoho Assist for its simplicity and robust security. The tool does not require installation and is compatible with the majority of antivirus solutions. You can establish a remote desktop session with a Linux machine in minutes.
Zoho Assist is free for personal use which allows you to start a remote support session, share your screen, and access and configure unattended network-attached devices.
Zoho Assist’s features include:
Instant Chat – Maintaining contact with a remote user helps a technician quickly identify and resolve problems.
- • File Transfer – Zoho Assist addresses some of the limitations with Linux hardware access by enabling the transfer of files up to 2GB in size between a customer and a support technician.
- • Reboot and Reconnect – All it takes is a click from their console for a technician to reboot and reconnect to a remote Linux machine.
- • Invite Technicians – The open source nature of Linux environments often requires multiple technicians to resolve complex issues. You can easily invite other techs to assist you during a ZoHo Assist support session.
- • Multi-Monitor Navigation – Zoho Assist makes it easy to navigate between multiple monitors while conducting remote support sessions.
13. AnyDesk Linux
The AnyDesk remote desktop client for Linux is a flexible solution that supports a wide range of Linux distributions. Supported distros for this RDP client include Ubuntu, Red Hat, and openSUSE. There is also a generic Linux version available for 32-bit or 64-bit systems.
AnyDesk for Linux minimizes desktop and server storage with small file sizes that result in fast downloads. You can get started and establish a Ubuntu RDP client in a few clicks by following the package manager. AnyDesk provides free updates and the feature set is constantly being updated. Cross-compatibility is never an issue, as all versions of the software are compatible with each other.
The AnyDesk remote desktop for Linux employs the DeskRT codec and offers users low latency, high frame rates, and efficient bandwidth utilization for fast response times. The remote desktop tool provides innovative technologies that work well with any application.
Military-grade TLS 1.2 encryption and RSA 2048 asymmetric key exchange encryption are used to ensure secure connectivity to remote computers. Support is also provided for using Linux remote access tools over the intranet on a private network.
As you can see, there are plenty of effective remote desktop Linux clients to choose from, all of which boast unique advantages that make them worth exploring.
We hope this post has instilled you with greater confidence and excitement to implement remote desktop client Linux tools into your workflow.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
A Linux remote desktop client is a software tool that allows a user to access and control a remotely located Linux computer over a local network or the Internet.
Power users should look for functions such as hotkeys, an intuitive interface, and customization options. Security, privacy, and the ability to support multiple sessions simultaneously are also factors to consider when selecting a Linux RDP client.