Main Types of VPN and Their Features
When determining the best solution to use, be aware that there are different types of VPN, each offering its own unique pros and cons. Some VPNs are better for tasks like getting around geo-blocking. Some of them are created to allow access to sensitive data remotely from a work server or computer. The others are better for streaming.
All the VPNs (Virtual Private Network) in general serve to secure your data while on the internet. It creates what is known as a tunnel between your device and the internet. This effectively creates a private network where all traffic is encrypted and the identities or IP addresses of the devices are hidden from the prying eyes of the general public. The transmitted data is only decrypted once it reaches the designated VPN server, and only the server’s IP is visible or known.
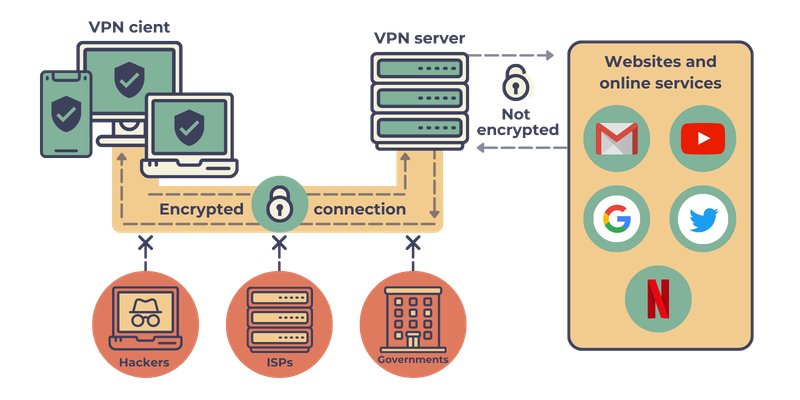
A VPN also allows corporate users to extend their network to remote locations which are especially useful for remote working.
VPN Is a Service or a Technology?
In general, VPN is considered a service provider offering users virtual private networks so they can access the internet with security and privacy. However, there’s a difference between VPN technology and VPN services. Let’s differentiate between them to grasp the concept better.
VPN technology: A virtual private network (VPN) provides a private, secure connection between a user’s device and the destination or endpoint. It encrypts and hides your web traffic by utilizing a VPN protocol. This way, it helps keep your data safe and protect your privacy. And the technology behind this is the VPN technology.
VPN services: A company may offer VPN services as a package with different types of VPNs and additional benefits included in it. Benefits like the ease of use through automatic setups and native clients, extra help such as configuration guides, customer support, knowledge base, FAQs, and more may be included in the services.
VPN services are like a virtual toolbox to improve and strengthen the internet connection. It may also have a range of gadgets and devices helpful during browsing sessions. These can include security features, VPN protocols, live chat support in real-time, auto-connect settings, and more.
That said, you could use only one of them at a time based on the service provider. But mostly, you can switch between a VPN service and technology through the VPN service. A good VPN provider will offer excellent VPN features and protocols, letting you choose a suitable one based on your needs.
Types of VPN as Technology
Here is a VPN classification scheme that is based on topology and then split based on the technology used:
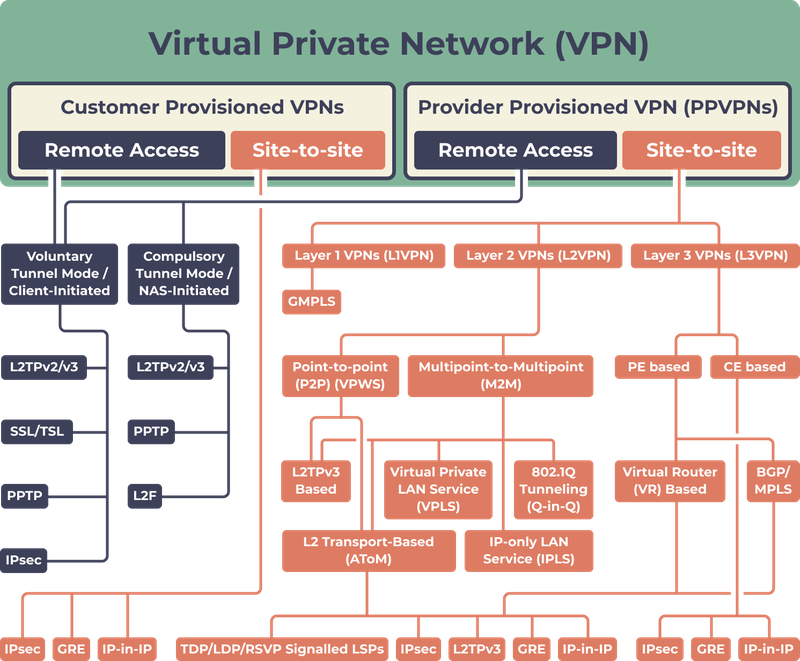
Let’s take a closer look at this diagram.
Type of VPN Provision
Provider Provisioned VPN
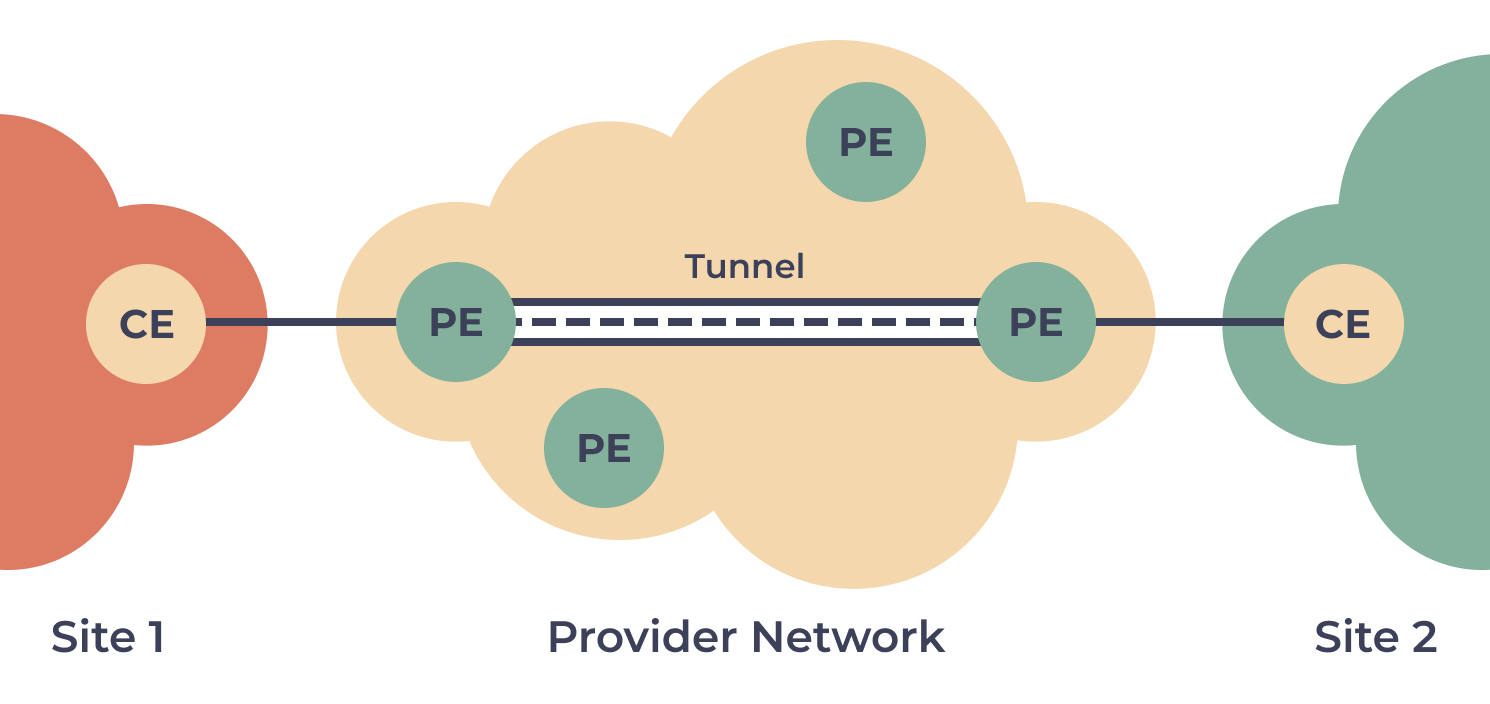
Provider Provisioned Virtual Private Networks (PPVPN) refers to enterprise-grade VPNs that businesses mainly use to allow employees to secure their remote access while entering the corporate network.
PPVPNs are even used for securing the connection between physically separate websites and networks over the internet. PPVPNs are provisioned and managed by a service provider.
The benefits of using PPVPNs include faster deployment, consistent security, reduced cost, and secure access to a company’s data center and cloud.
Customer Provisioned
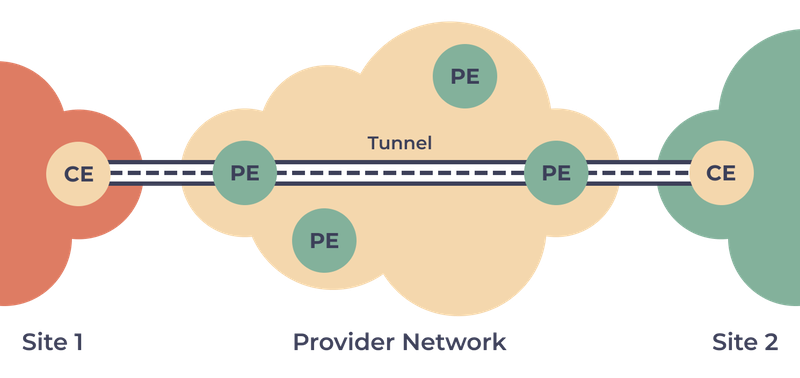
In customer provisioned VPNs, a user can create and manage a VPN by themselves. Here, the tunnel is set up between a remote user and the company gateway.
Customer provisioned VPNs are not peer-model since the service provider has no idea about a VPN that the user has self-created.
The advantage of this type of VPN includes the user’s independence from a service provider who only provides the internet connection to the user to access the company gateway.
Type of VPN Connection
There are mainly two types of VPN connections – remote access VPNs and site-to-site VPNs. Both of them offer solutions to solve similar problems but the methods are different. They both aim at protecting organizational resources and data from unauthorized access.
Let’s understand them one by one.
Remote Access VPN Technology
Remote access VPN is a technology where a connection is temporarily encrypted between a user’s device and a company’s data center. This connection becomes active once the user has enabled it, else it won’t, since it has no permanent link.
Businesses majorly use this VPN technology to access data and applications stored in a hub securely through a VPN tunnel. It’s like a VPN connection that makes a safe pathway to accessing company resources and sensitive data from your computer.
The best remote access VPN offers advanced features and functionalities. They are suitable for classified documents and self-hosted applications that you don’t want to host anywhere else. However, if you have more users, you would require more capable hardware. So, plan beforehand according to the number of users accessing the VPN.
Site-to-site VPN Technology
The site-to-site VPN technology offers a permanent connection between several offices, creating an always-available, uniform network. This type of VPN requires separate network configuration on both ends. It’s suitable if you run multiple remote websites. Site-to-site VPNs are configurable on both firewalls and on-premises.
Furthermore, site-to-site VPN technology is an affordable method for merging separate networks and forming an intranet. In this network, each device functions like it’s on the same network, enabling information exchange. It also secures the network from external threats. However, the VPN technology is not ideal for users connecting from home, since administrators can’t control external connections and security risks may arise.
Site-to-site VPN is of two types:
- • Extranet-based site-to-site VPN: This VPN connects websites belonging to several organizations.
- • Intranet site-to-site VPN: It involves a network configuration where the websites connected with the help of a VPN are from a single organization.
Layers
A VPN connection can be established at various layers. They are:
- • Layer 2: In this layer, ethernet frame exchange happens in the VPN:
- ◦ Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) virtualizes a given leased line in a network where packets are switched.
- ◦ Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS) virtualizes a local area network (LAN). Here, terminals are linked like they are from the same LAN with broadcast packets.
- ◦ IP-only LAN-like Service (IPLS) virtualizes a given IP network, allowing only IP (ARP and ICMP) packets.
- • Layer 3: In this layer, IP packet exchange happens in the VPN.
- • Layer 4: In this layer, TCP or SSL connections are established in the VPN.
Types of VPN as Service
VPN software can be grouped into the following four use cases:
- • Personal services
- • Remote access
- • Mobile
- • Site-to-site access
Each use case is documented in the table below with a brief description of the type of user it’s best suited for, as well as the primary purpose of each VPN software type.
VPN types | ||||
Who uses | Private users connecting to a private network | Private users connecting to a private network | Allow networks to connect to other networks | Allow users to connect to a network using third-party servers |
Primary purpose | To connect remotely to a work network or any other network. | Allow for consistent network connection despite an unstable internet connection. | Extend your network by joining multiple networks | Increase your internet security and protect against DDoS attacks. |
Common use case examples | Where the nature of work requires an employee to travel, they can still access the company network from anywhere. | A VPN is especially useful in areas of poor connectivity. This extends the option of working remotely to more of your workforce. | Сompanies that have different branches can keep them all connected using site-to-site VPN.
| Personal VPN is most often used to bypass geographic restrictions. For example, live sports streaming may be restricted to European regions.
|
Wide used protocols | DMVPN technology; IPsec tunnel; MPLS based L3VPN | |||
Examples of each VPN type available | Mobile VPN is a form of business VPN and usually includes Bittium SafeMove Mobile VPN and Radio IP software | Cisco’s Dynamic MultiPoint VPN; Multi-Protocol Label Switched (MPLS) Layer 3-based VPNs |
Keep reading to learn more about VPN Types
Site-To-Site VPN
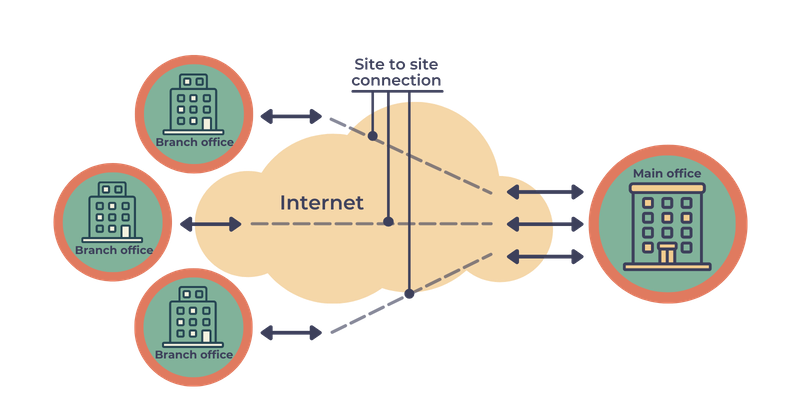
The most common need for a site-to-site VPN is with large corporations with branches spread across multiple locations. A site-to-site VPN will make it possible to connect the different networks together. That is the core difference between a site-to-site VPN and a remote access VPN.
Companies can therefore facilitate the sharing of resources across all the various company networks without relying on a multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) circuit which links routers together across networks.
There are two kinds of site-to-site VPNs available:
Intranet-Based VPN: This is the term used to describe a situation where all the networks that are being connected belong to one company. The company can then create a single wide area network (WAN) encompassing all of these internal networks making it possible for the workforce to connect to any network seamlessly.
Extranet Based VPN: This is for connecting to a network belonging to a different company. A use case may be when your staff has a requirement to connect to a supplier directly to have access to real-time stock levels.
Connecting multiple networks is a complex operation and it requires the correct hardware as well as know-how. Some available solutions include Nokia VPRN service (L3VPN) and Cisco’s Dynamic MultiPoint VPN (DMVPN).
Remote Access VPN
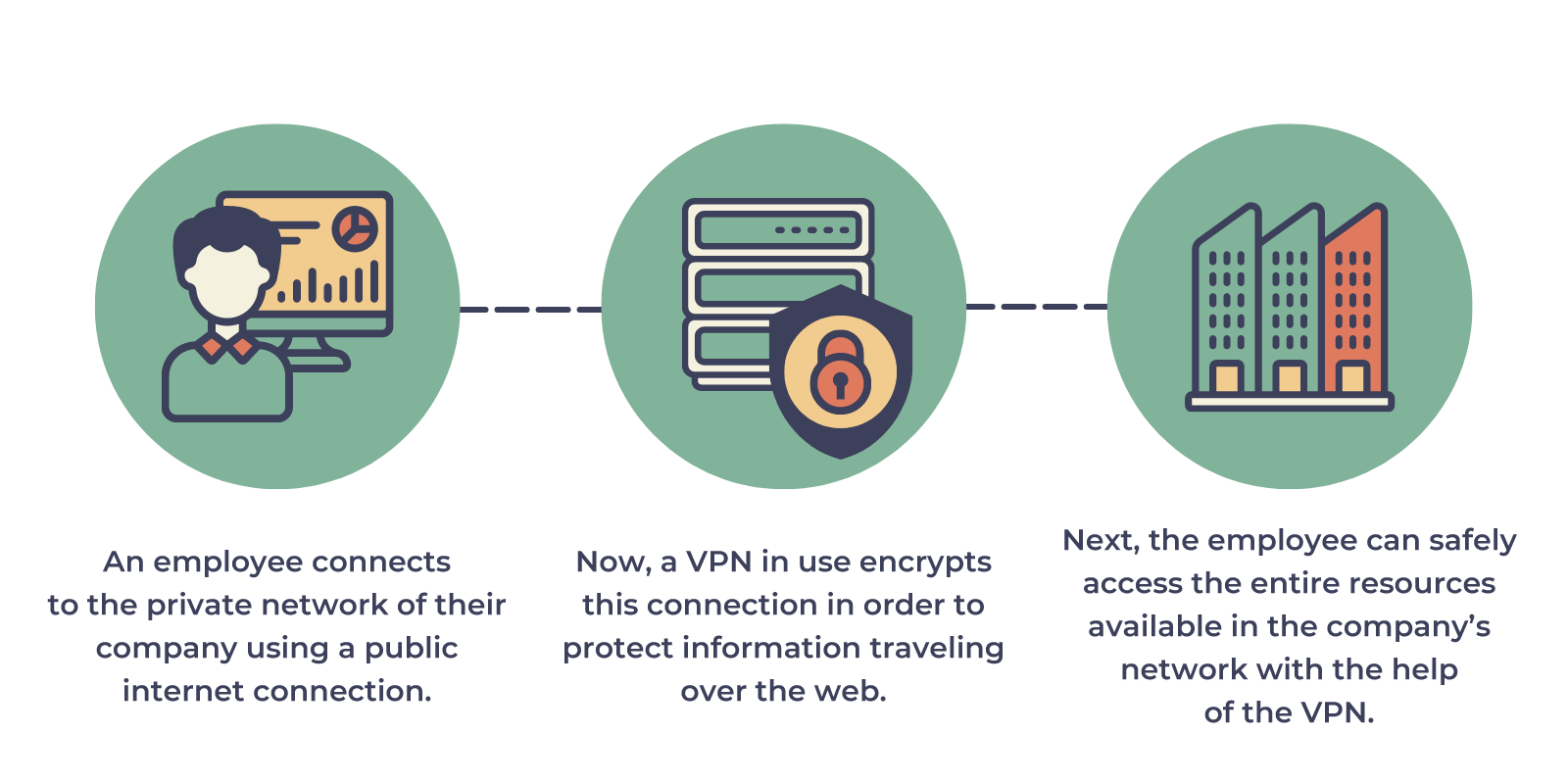
The primary use of a remote VPN is to create a secure connection to a corporate network. In essence, a VPN creates a tunnel which serves as a private connection so that even though you are connecting to a public internet connection, all data transmitted between the authorized remote client and the server is encrypted, thus allowing peace of mind that the company’s data is safe from prying eyes.
IPsec and SSL are two of the most common VPN protocols used to set up encryption.
VPN is however not geared towards the move toward cloud-based services. Traditionally developed for access to data centers for users located in close proximity, but now with the increase in remote working, employees are located further afield and latency becomes a problem as the performance level drops as the physical distance increases between the two points.
Good examples of remote VPN: OpenVPN Access Server; Perimeter 81 Next-Gen Secure VPN Solutions, NordLayer VPN.
Mobile VPN
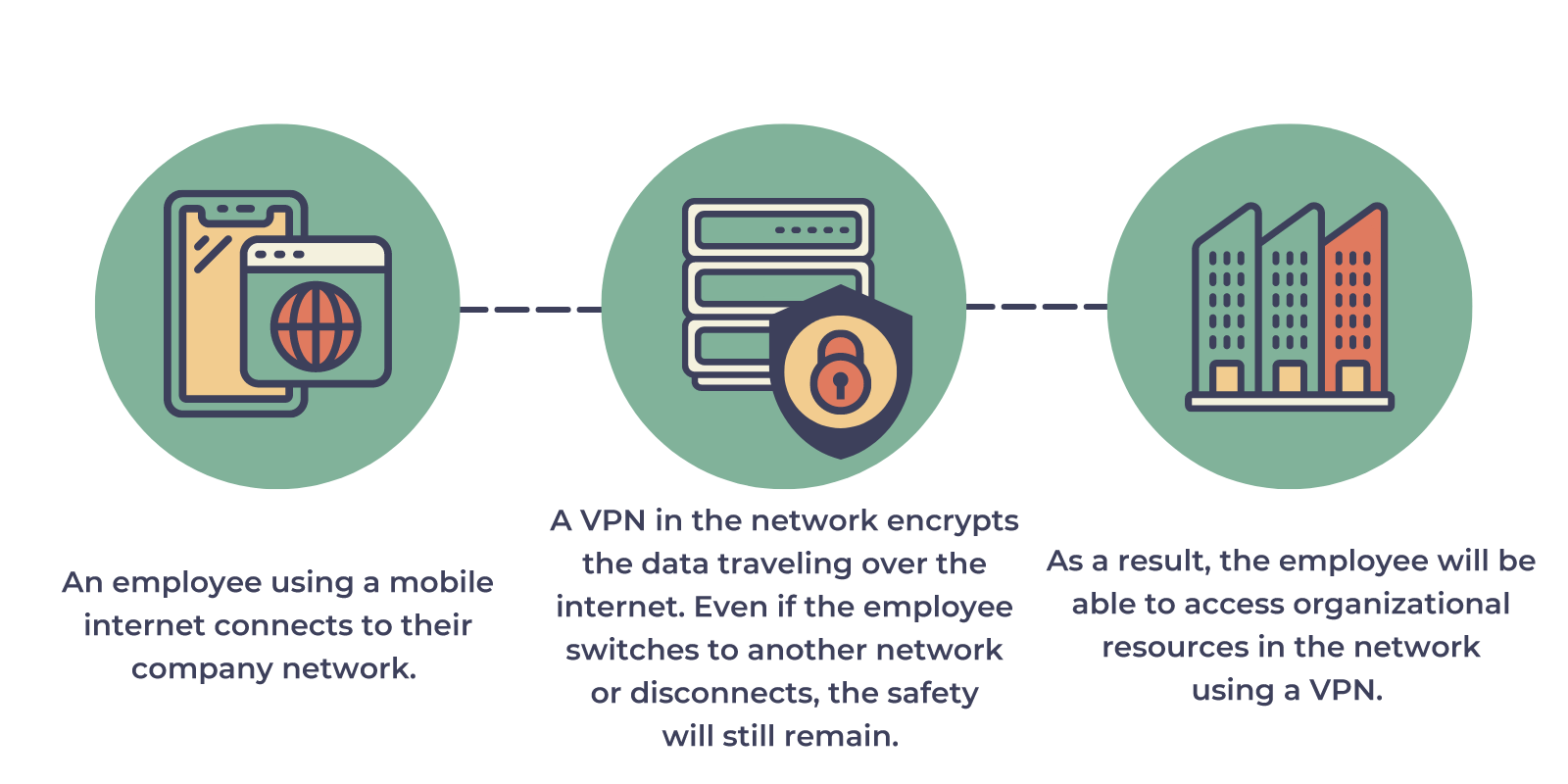
The name Mobile VPN may cause confusion as a VPN can be used on any device including your mobile phone. In this case, it is sometimes incorrectly called a Mobile VPN. The “mobile” part actually refers to the ability to change your connection or if the connection drops, the virtual network connection stays connected.
Imagine a case where an employee is connected remotely via their laptop while off site at a client using mobile data. They then return to their home office where they connect to the Wi-Fi – despite an IP address change, or the interim connection drop, their safe encrypted connection to the office persists.
Good examples of Mobile VPN: WireGuard, Nord VPN; Bittium SafeMove Mobile VPN and Radio IP software.
Personal VPN
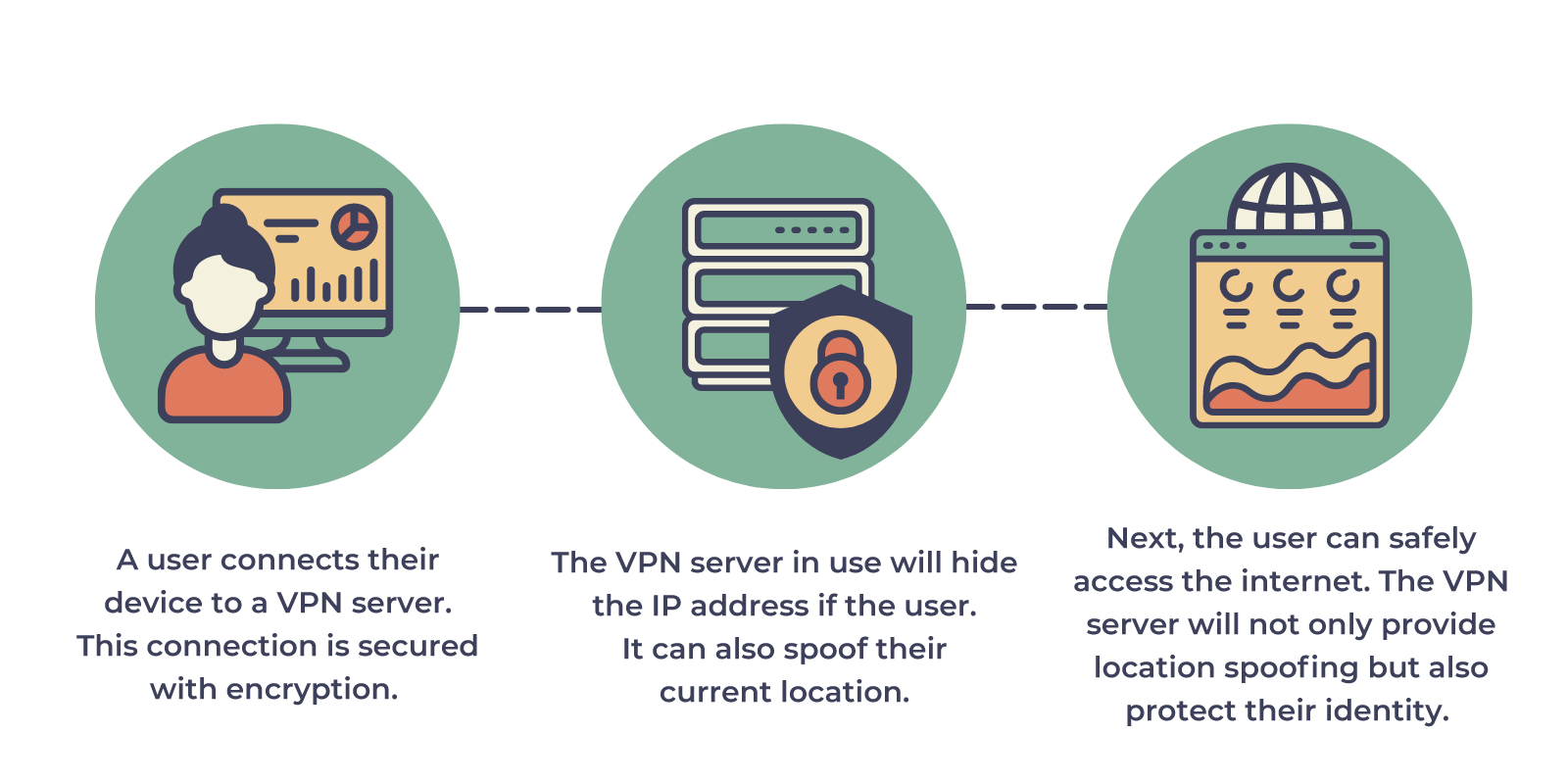
Protecting your personal data while online and accessing geo-restricted content are two of the main reasons why you might want to make use of a personal VPN.
How does a personal VPN benefit you?
- • You can access otherwise restricted content as it spoofs your physical location so it appears as if you are connecting from an allowed region.
- • Hide the fact that you are streaming games to prevent service providers from throttling your connection.
- • Thanks to the anonymity, your online activity can not be monitored.
- • If you live in a country the imposes internet restrictions, i.e. China with their “firewall” that monitors and blocks certain internet sites – you can bypass this using a VPN.
Good design of personal VPN: OpenVPN, WireGuard, or ExpressVPN’s proprietary Lightway protocol. Depending on what purposes you have you might choose a more secure OpenVPN or faster ExpressVPN.
Other Types of VPN Classification
Based on the pricing and features, VPNs can be divided into several types.
Free, Budget, and Premium VPN Properties
There are different solutions on the VPN market ranging from free to expensive premium solutions. Should you pay more, and which type is right for you? Let’s figure it out.
Free VPNs
If your internet access requirements are minimal, you may want to go with free VPNs. Although they are great for casual use, they involve security risks and various restrictions.
So, choose this option only if you are in need of a VPN but don’t have the budget for it.
Budget VPNs
As the name says, budget VPNs are affordable VPN services with price being their biggest plus point. So, if you need VPNs but your budget is low, go for it. It’s great for small businesses, startups, and individuals.
There are many VPN providers that offer budget VPNs while some of them even have features available in premium VPNs. Good examples of budget VPNs include PrivateVPN, Private Internet Access, etc. They offer features like high speed, customer support, kill switch, proxy support, and more.
Premium VPNs
These VPNs are offered by most leading VPN providers. These VPNs offer a high level of performance, security, privacy, and features.
Premium VPNs offer many advantages such as intuitive clients for major platforms, live chat, responsive and helpful customer support, multi-protocol support, a large number of high-end servers in multiple locations and countries, and more. These VPNs not only offer high speeds but also greater reliability.
Given the offerings, premium VPNs are expensive, especially in their monthly plans. They are a good investment with all the benefits you get. These are best suitable for enterprises and SMBs.
A good example of a premium VPN provider is ExpressVPN. It’s known in the market for providing incredibly fast speeds with useful features such as anti-DDoS servers, split tunneling, countering VPN blocks with obfuscation, etc.
Premium and budget VPNs are different majorly on the basis of the fact that premium VPNs provide a complete VPN package while budget VPNs provide affordable services including only the essential features and functionalities.
How to Choose the VPN Type Right for You?
If you are confused, here’s something we are going to recommend.
- • Choose premium VPNs if you have the budget and the need for an advanced VPN to carry out your work. If you are an enterprise and a large-sized business, you may go with it.
- • Choose budget VPNs if you are on a tight budget but still need a VPN to access the web with security. Go for this, if you are a small or medium size business.
- • Choose free VPNs if you are an individual or a startup that needs a VPN for casual work.
A word of caution:
While it may be tempting to save some money and use a free VPN, bear in mind the associated risks with this. There have been cases where users’ personal data and their internet activity become a commodity and it’s sold either for marketing purposes or other nefarious activities.
Multi-Protocol or Single-Protocol
Multi-protocol VPNs are VPN services offering multiple VPN protocols that users can choose from. These are versatile and give you the option to decide the VPN software aspect that’s more desirable to users at a time and work on increasing its efficiency. These are best for a variety of purposes, like gaming, messaging, streaming, and torrenting.
Single-protocol VPNs: These VPNs support only one VPN protocol defined by the design philosophy or limited resources.
If you are to choose one among them, multi-protocol VPNs are a better choice.
If you encounter a scenario where your VPN slows down your internet connection, use split tunneling, change the protocol, or try connecting to a closer server that is not overloaded. Also, if you are finding the reasons your VPN is not connecting
, you may want to restart the connection.
Conclusion
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) help you access the web with better security and privacy, no matter what site or page you want to view. There are different types of VPNs, both as technology and service. Thus, choose the type of VPN based on your individual or organizational needs and continue exploring and leveraging the web to its fullest.
Thus, choose the type of VPN based on your individual or organizational needs and continue exploring and leveraging the web to its fullest.