Why VPN won’t connect When Working From Home? Fix all Issues in 10 Steps
A VPN is necessary to browse the internet securely and without disruptions due to access limitations. However, even VPN is not connecting for a number of reasons. Therefore, it is important that you know how to fix your VPN connection on your own especially when it’s essential for your work or business. In this article, we’ll cover various ways how you can fix your VPN connection issues while you’re at home.
VPN Troubleshooting List
First of all VPN issues may originate from your service provider’s side. To make sure that a scheduled service interruption did not cause the issue. Check your e-mail first for any missed announcements.
- Check your internet connection
- Check your login credentials
- Check your VPN settings
- Restart the VPN software
- Make sure your software is up to date
- Check your IP address
- Allow VPN ports, protocols, and passthrough
- Your router and your VPN should be compatible
- Change the VPN tunneling protocol
- Check your Firewall
1. Check Your Internet Connection
The first thing that you should do before performing other fixes is to check your internet connectivity. Your device needs to be connected to a reliable Internet connection for your VPN to run properly. If the network connection between your computer and the VPN server was interrupted, it is either an error on your ISP’s end or your end.
Here are some ways that can help you check your internet connectivity:
- First, make a quick and simple Internet search. If your browser successfully loads the site, then you’re good to go. However, if it displays a message like “Unable to connect to the Internet,” then you’re not connected to the Internet.
- If you’re using a LAN connection, make sure that the ethernet cable is connected properly to your device and the router. Replace the cable if faulty.
- Try removing your current Wi-Fi profile and reconnecting. Make sure you have the right password.
- If none of the above solutions work, call your internet service provider.
2. Check Your Login Credentials
The reason why your VPN is not working may be because of outdated login credentials. To change or update your login credentials, you can go to your VPN’s dashboard and access your account settings.
3. Check Your VPN Settings
Make sure that your VPN is configured to the right settings provided by your IT department, such as your Port and DNS settings.
Port Settings
Certain ports are denied access to traffic by some ISPs and networks. If you have the wrong Port, this may be the reason why your VPN is not functioning as intended.
First, you should check your VPN’s documentation for the right port number. Port settings differ depending on the VPN you’re using. If you’re using Nord, then you should be on 443 TCP and 1194 UDP ports to gain access to traffic.
WireGuard uses UDP port 51820, while IKEv2 uses 4500 and 500. Make sure that you’re using your VPN’s designated port by reading provided instructions.
DNS Settings
Try changing to a different DNS server address. If you’re experiencing VPN issues working from home, you may be on the wrong DNS address, or your service provider’s DNS server might be unresponsive or dealing with technical difficulties.
However, you should know that using custom DNS servers can expose you to leaks.
Change VPN Server Locations
If possible, change to a different server. If you are unsure which server to connect to, contact your IT department. Connecting to some locations may prevent you from accessing your company’s network.
4. Restart the VPN Software
Try restarting the VPN software. Don’t just close it and leave it running in the background, but terminate the whole process.
If you’re using a VPN plugin on your browser, try clearing your browser’s cache and reopening it. If this doesn’t work, try using a different browser, as your current browser may not be compatible with your VPN plugin. You can also try using another device with a different browser.
5. Make Sure Your Software Is Up to Date
It is important that you keep your VPN software up to date to eliminate bugs and security risks. Regular updates are performed by your service providers to keep your VPN experience delightful. To make updates more manageable, you can go to your VPN software’s settings and turn on automatic updates.
To ensure that the VPN issue is not caused by a browser-related problem, only use browsers recommended by your VPN provider. Also, keep your browser up to date.
6. Check Your IP Address
Your IP address may belong to the same subnetwork as your company’s, which may be why you’re having problems with your VPN not connecting. This can easily be fixed by simply changing your IP address’s subnetwork.
First, open your router’s settings through your browser. Then, make sure you have the right login credentials and the right IP address. To determine what your IP address is, open your Command Prompt and type IPCONFIG (For Windows). For Mac users, you can find your IP address in your device’s System Preferences under the Network tab.
Once logged in, go to your router’s configuration page and change your IP address, wherein the first 3 blocks are not identical to your company’s subnetwork. For example, if your IP address is 192.165.2.1 and you have the same subnet as your company’s, then change it to 192.165.1.1.
7. Allow VPN Ports, Protocols, and Passthrough
To enable VPN ports, protocols, and passthrough, go to your router’s settings by entering your IP address on your browser. After logging in, locate your router’s firewall and security settings.
Under these tabs, you’ll be able to find VPN port forwarding, protocols, and passthrough options. If you don’t know what your login credentials are to open your router settings, check the back side of your router.
If you have tried all the solutions above and you’re still experiencing troubles with your VPN not connecting, it’s possible that your router is to blame. To make your router work with your VPN client, you can try any of the steps below:
Enable VPN passthrough. Doing this will help your router distinguish VPN traffic and allow it to establish an outbound VPN connection. Most routers today, especially newer models, will have a VPN passthrough option. However, this option is not enabled automatically all the time. If this is the case, you can easily allow it through your router’s settings. If you own a TP-LINK router, you can follow the steps below:
- To get started, go to your router’s Security settings. Then, in the control panel, click on Security in the right-hand side panel
- Under Security, select Advanced Security
- Next, proceed to NAT Forwarding, then select ALG
- Enable PPTP passthrough, L2TP Passthrough, and IPSEC Passthrough
In some models, after accessing the Advanced Security settings, you’ll be able to find the PPTP/L2TP/IPSec Passthrough under the VPN section.
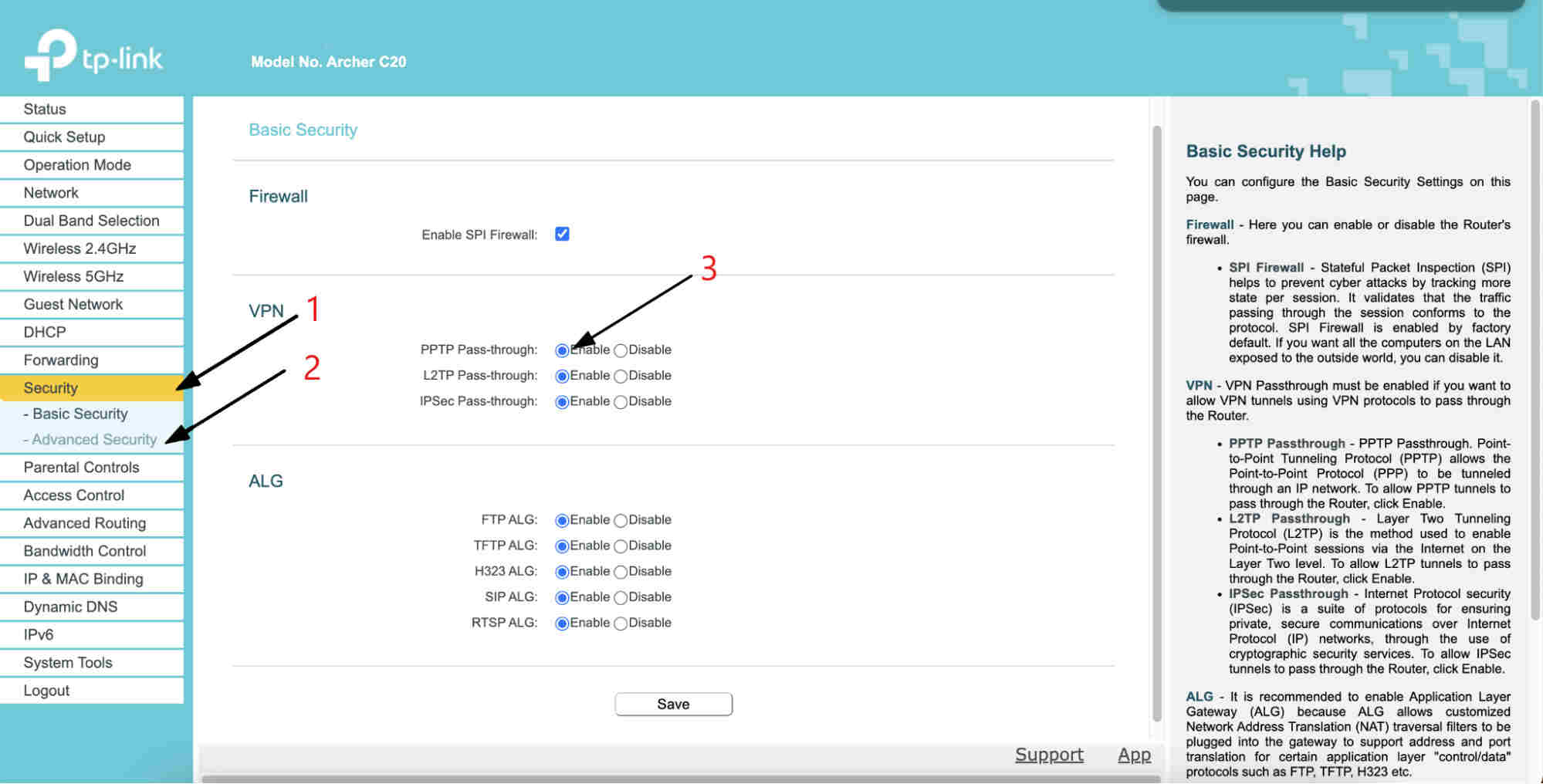
Note: These options may not be available in some routers.
Port and protocol forwarding. You may or may not need to do this depending on your router model and network settings, but this can help you enable needed ports and protocols for you to establish a VPN connection.
- • TCP/UDP port 53 for Private DNS services
- • UDP ports 500 and 4500 for L2TP/IPSec. You will need to enable IP protocols 50 and 51 before unblocking UDP port 500/4500
- • UDP ports 500 and 4500 for IKEv2
- • UDP port 1194 for OpenVPN
- • TCP 443 for SSTP. This protocol is not advisable for use. There are better alternatives that you can check out
- • TCP port 1723 and GRE protocol for PPTP. Using the PPTP protocol is unsafe. Switch to more secure protocols
- • WireGuard uses UDP port 51820
Note: All VPN services have their own proprietary protocol. You can access this information in your VPN’s documentation. If the above list did not help you with your VPN connection, you could always contact your Internet Service Provider for assistance. Your ISP may have blocked any of the ports mentioned.
8. Your Router and Your VPN Should Be Compatible
There are some routers that are incompatible with certain VPNs. If this is the case, you can buy a new one or combine another router with your current one.
On the other hand, there are also some routers that are VPN-ready but need to undergo a VPN passthrough, which is a feature of some routers that allows you to access a VPN without it being blocked. If you do not know your router’s VPN compatibility, contact your IT department for help or assistance.
9. Change the VPN Tunneling Protocol
If none of the solutions above work, try to tunnel your VPN. You go to your VPN or network settings to change your VPN protocol. If you’re using OpenVPN, you can use TCP instead of UDP. Hit the link if you want to learn which VPN protocol is best for your purposes.
10. Check Your Firewall
Your firewall may be blocking your VPN from running and causing unwanted VPN errors. It may be because it is recognizing it as a threat or it is seeing incoming traffic as unusual or weird.
To confirm this, you can temporarily turn off your Firewall and see if your connections are fixed. If this is the case, your next step would be to open some outgoing ports.
How Organizations Can Improve VPN Experience for Remote Workers
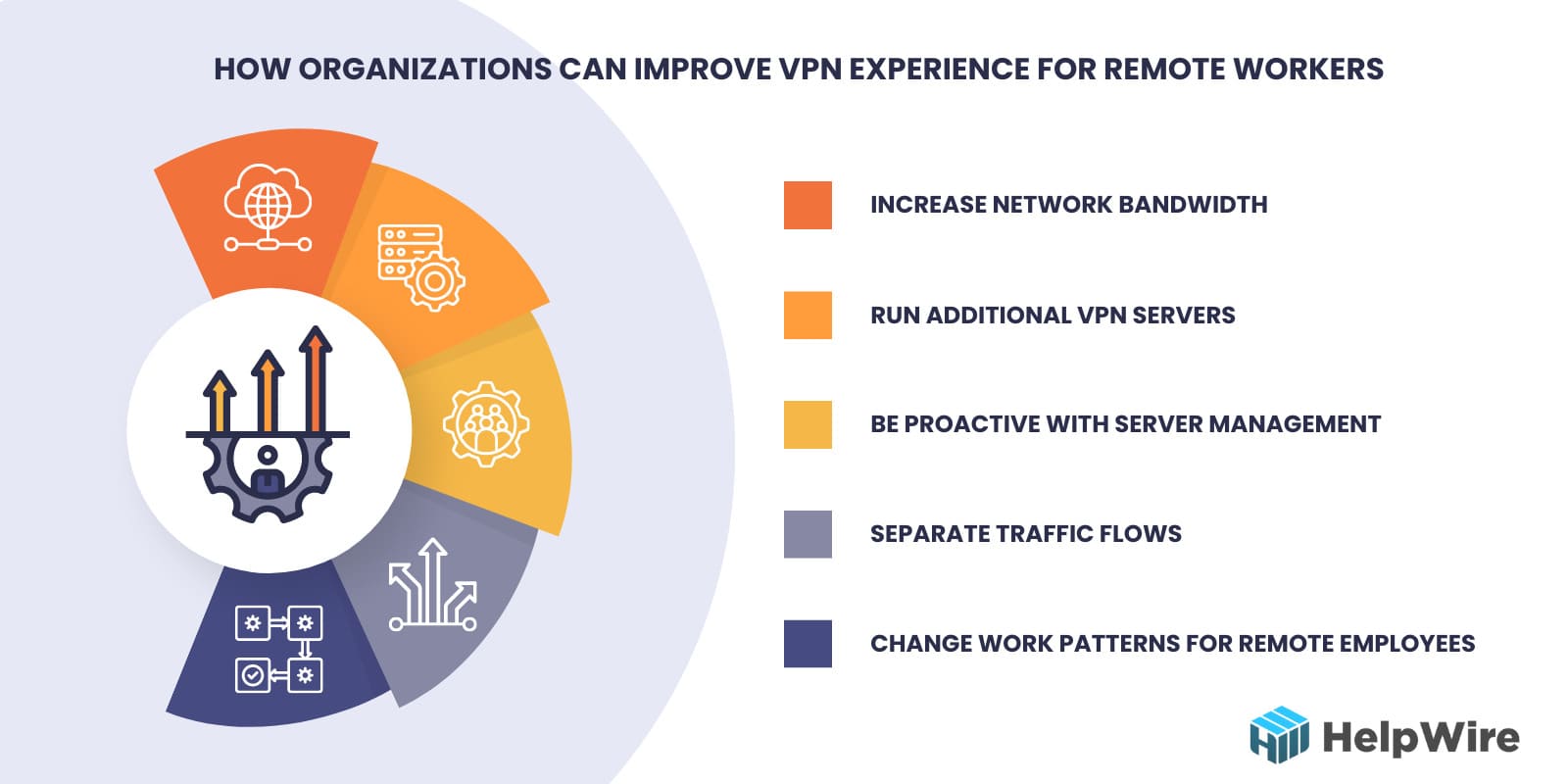
There are a number of things the organization can do to improve the user experience when connecting via a VPN:
Increase Network Bandwidth
By increasing the available bandwidth between the VPN server and the internet, the overall latency experienced is much less.
Run Additional VPN Servers
It makes sense that having additional VPN servers increases capacity, but implementing load balancing across the servers will result in a more robust and reliable experience for your employees, where they can be routed to the server that can serve them best at any given time based on load and capacity.
Be Proactive with Server Management
Server maintenance must be an integral part of your organization’s network strategy. All upgrades and patches must be applied timeously to ensure your servers are protected against ever-changing security threats.
Separate Traffic Flows
Split tunneling allows you to route some data through the VPN while other data is routed through normal public unsecured lines. The benefit of this is a reduction in bandwidth usage and connectivity speed.
This is a common problem where a VPN slows down your internet. Actions that would normally not need to be secured, like simple internet browsing, do not require encryption, whereas confidential business emails and documents will require a secure tunnel.
Change Work Patterns for Remote Employees
Another simple way to make a VPN work more efficiently is to change how your employees work. It’s not always necessary to edit a document or view a resource online on the remote server. Rather download the required resource, make the required changes, and then upload it. This uses a lot fewer VPN resources.
Companies can also introduce staggered working hours or shifts to reduce the number of concurrent connections to the VPN, thereby reducing the load and improving the performance.
Conclusion
VPN services are very important in today’s time when digital transformation is at its peak, and the work-from-home setup is becoming the norm. Thus, knowing how to fix a bad VPN connection is a skill that everyone should learn knowing that a VPN app doesn’t work flawlessly all the time.
If the above tips and solutions still can’t fix your VPN, contact your IT department or your service provider for support, or perhaps you should choose the better remote access VPN for business out there.
FAQ
Why Does VPN Not Connect on My Phone?
Invalid subscription
If you can’t access your VPN network, this may be because of an expired subscription. To fix this, you can simply renew your plan.
- Open your VPN client > Settings
- Click on your Account/Profile Settings
- Look for your subscription expiry date
- If your subscription has expired, renew your plan
Server Outage
With a VPN, you can connect to hundreds of servers worldwide. If your connection is not working, this may be because the server you’re connected to is down.
- Launch your VPN client
- Go to your Locations tab
- Select another location
- Try reconnecting to your VPN network again. If this does not work, try other solutions
You haven’t set app permissions
After installing the VPN app on your mobile phone, you should first give it permission to access your device before you can connect to your VPN.
- Launch the VPN app
- Set up a VPN connection
- After attempting to connect to a VPN network, a dialog box will appear asking if you want to allow the connection request. Select OK
Slow or no internet connection
Before you can establish a VPN connection, you’ll first need to be connected to the Internet. If you have slow Network speeds or you have been disconnected from the Internet, you won’t be able to connect to your VPN
- Reset your Internet Connection
- Go to your quick toggles menu
- Enable and disable Airplane mode
- Once you have re-established your connection to the Internet, try connecting to your VPN again
- If it still doesn’t work, test if your internet connection is working with apps like Speedtest
How to Fix VPN not Connecting to WiFi
- Check your VPN connection. If you aren’t connected to your VPN, try reconnecting.
- Disable security protocols on your WiFi network. Then, try reconnecting to your VPN. If this doesn’t work, make sure that you enable the security settings again.
- Switch to another VPN server if you’re on public WiFi. Some public WiFIs have certain types of VPN traffic blocked, which may be the reason why you’re unable to connect.
- If none of these solutions work, contact your VPN’s customer support. They may be able to guide you through the issue or fix it from their end.